没有sudo权限,如何在full system模式下运行spec2017:
- build spec2017 with linux kernel,这一步如果没有sudo权限在自己的笔记本上装个虚拟机build,这一步需要gem5resource,packer,qemu,编译好image之后,后面就不需要了。编译spec2017 编译parsec
- build完毕之后,如果有sudo 权限的话,可以boot linux kernel使用kvm加速,但是因为我没有,所以就不需要qemu,kvm;在boot阶段直接使用atomic模式,之后switch到timing模式。
- 不需要使用gem5art和gem5resources,没有sudo权限的话,搞定这两个工具也十分痛苦。
- 使用的脚本为configs/example/gem5_library/x86-spec-cpu2017-benchmarks.py 这里面require KVM是true,改成false;boot阶段使用kvm,也改成atomic cpu。还有就是如果atomic cpu,和ruby的cache 配合有问题,需要把cache的改一下,就ok了。
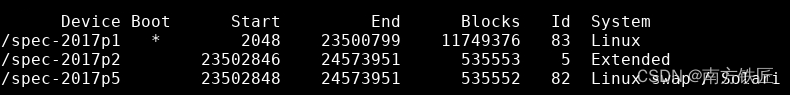
- 由于image partition的问题,如果不传入partition的参数,gem5会报告kernel panic。gem5 full system Linux boot fails with “Kernel panic – not syncing: VFS: Unable to mount root fs” 这时候可以fdisk 这个image文件,blocks最多的那个就是需要的partition。因此传入的参数加入了partition=1。
主要还是明确了不需要的东西 ,在build spec2017 image之后,就不需要gem5art和gem5 resources了。
最后命令行如下:
build/X86/gem5.fast -re --outdir=./m5out/bwaves/fullsystem configs/example/gem5_library/x86-spec-cpu2017-benchmarks-atomic.py --image=/proj/snic2021-5-411/users/x_qisha/proj/gem5-resources/src/spec-2017/disk-image/spec-2017/spec-2017-image/spec-2017 --benchmark=603.bwaves_s --size=test --partition=1
具体内容如下:
# Copyright (c) 2021 The Regents of the University of California.
# All rights reserved.
#
# Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
# modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
# met: redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer;
# redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
# documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution;
# neither the name of the copyright holders nor the names of its
# contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
# this software without specific prior written permission.
#
# THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
# "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
# LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
# A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
# OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
# SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
# LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
# DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
# THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
# (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
# OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
"""
Script to run SPEC CPU2017 benchmarks with gem5.
The script expects a benchmark program name and the simulation
size. The system is fixed with 2 CPU cores, MESI Two Level system
cache and 3 GB DDR4 memory. It uses the x86 board.
This script will count the total number of instructions executed
in the ROI. It also tracks how much wallclock and simulated time.
"""
import argparse
import time
import os
import json
import m5
from m5.objects import Root
from gem5.utils.requires import requires
from gem5.components.boards.x86_board import X86Board
from gem5.components.memory import DualChannelDDR4_2400
from gem5.components.processors.simple_switchable_processor import(
SimpleSwitchableProcessor,
)
from gem5.components.processors.cpu_types import CPUTypes
from gem5.isas import ISA
from gem5.coherence_protocol import CoherenceProtocol
from gem5.resources.resource import Resource, CustomDiskImageResource
from m5.stats.gem5stats import get_simstat
from m5.util import warn
from m5.util import fatal
# We check for the required gem5 build.
requires(
isa_required=ISA.X86,
coherence_protocol_required=CoherenceProtocol.MESI_TWO_LEVEL,
kvm_required=False,
)
# Following are the list of benchmark programs for SPEC CPU2017.
# More information is available at:
# https://www.gem5.org/documentation/benchmark_status/gem5-20
benchmark_choices =["500.perlbench_r", "502.gcc_r", "503.bwaves_r",
"505.mcf_r", "507.cactusBSSN_r", "508.namd_r",
"510.parest_r", "511.povray_r", "519.lbm_r",
"520.omnetpp_r", "521.wrf_r", "523.xalancbmk_r",
"525.x264_r", "527.cam4_r", "531.deepsjeng_r",
"538.imagick_r", "541.leela_r", "544.nab_r",
"548.exchange2_r", "549.fotonik3d_r", "554.roms_r",
"557.xz_r", "600.perlbench_s", "602.gcc_s",
"603.bwaves_s", "605.mcf_s", "607.cactusBSSN_s",
"608.namd_s", "610.parest_s", "611.povray_s",
"619.lbm_s", "620.omnetpp_s", "621.wrf_s",
"623.xalancbmk_s", "625.x264_s", "627.cam4_s",
"631.deepsjeng_s", "638.imagick_s", "641.leela_s",
"644.nab_s", "648.exchange2_s", "649.fotonik3d_s",
"654.roms_s", "996.specrand_fs", "997.specrand_fr",
"998.specrand_is", "999.specrand_ir"
]
# Following are the input size.
size_choices = ["test", "train", "ref"]
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="An example configuration script to run the \
SPEC CPU2017 benchmarks."
)
# The arguments accepted are: a. disk-image name, b. benchmark name, c.
# simulation size, and, d. root partition.
# root partition is set to 1 by default.
parser.add_argument(
"--image",
type = str,
required = True,
help = "Input the full path to the built spec-2017 disk-image."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--partition",
type = str,
required = False,
default=None,
help = "Input the root partition of the SPEC disk-image. If the disk is \
not partitioned, then pass \"\"."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--benchmark",
type = str,
required = True,
help = "Input the benchmark program to execute.",
choices=benchmark_choices,
)
parser.add_argument(
"--size",
type = str,
required = True,
help = "Sumulation size the benchmark program.",
choices = size_choices,
)
args = parser.parse_args()
# We expect the user to input the full path of the disk-image.
if args.image[0] != "/":
# We need to get the absolute path to this file. We assume that the file is
# present on the current working directory.
args.image = os.path.abspath(args.image)
if not os.path.exists(args.image):
warn("Disk image not found!")
print("Instructions on building the disk image can be found at: ")
print(
"https://gem5art.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorials/spec-tutorial.html"
)
fatal("The disk-image is not found at {}".format(args.image))
# Setting up all the fixed system parameters here
# Caches: MESI Two Level Cache Hierarchy
from gem5.components.cachehierarchies.classic.\
private_l1_private_l2_cache_hierarchy import (
PrivateL1PrivateL2CacheHierarchy,
)
cache_hierarchy = PrivateL1PrivateL2CacheHierarchy(
l1d_size="32KiB", l1i_size="32KiB", l2_size="512KiB"
)
#from gem5.components.cachehierarchies.ruby.\
# mesi_two_level_cache_hierarchy import(
# MESITwoLevelCacheHierarchy,
#)
#cache_hierarchy = MESITwoLevelCacheHierarchy(
# l1d_size = "32kB",
# l1d_assoc = 8,
# l1i_size="32kB",
# l1i_assoc=8,
# l2_size="256kB",
# l2_assoc=16,
# num_l2_banks=2,
#)
# Memory: Dual Channel DDR4 2400 DRAM device.
# The X86 board only supports 3 GB of main memory.
memory = DualChannelDDR4_2400(size = "3GB")
# Here we setup the processor. This is a special switchable processor in which
# a starting core type and a switch core type must be specified. Once a
# configuration is instantiated a user may call `processor.switch()` to switch
# from the starting core types to the switch core types. In this simulation
# we start with KVM cores to simulate the OS boot, then switch to the Timing
# cores for the command we wish to run after boot.
processor = SimpleSwitchableProcessor(
starting_core_type=CPUTypes.ATOMIC,
switch_core_type=CPUTypes.TIMING,
isa=ISA.X86,
num_cores=2,
)
# Here we setup the board. The X86Board allows for Full-System X86 simulations
board = X86Board(
clk_freq="3GHz",
processor=processor,
memory=memory,
cache_hierarchy=cache_hierarchy,
)
# SPEC CPU2017 benchmarks output placed in /home/gem5/spec2017/results
# directory on the disk-image. The following folder is created in the
# m5.options.outdir and the output from the disk-image folder is copied to
# this folder.
output_dir = "speclogs_" + ''.join(x.strip() for x in time.asctime().split())
output_dir = output_dir.replace(":","")
# We create this folder if it is absent.
try:
os.makedirs(os.path.join(m5.options.outdir, output_dir))
except FileExistsError:
warn("output directory already exists!")
# Here we set the FS workload, i.e., SPEC CPU2017 benchmark
# After simulation has ended you may inspect
# `m5out/system.pc.com_1.device` to the stdout, if any.
# After the system boots, we execute the benchmark program and wait till the
# `m5_exit instruction encountered` is encountered. We start collecting
# the number of committed instructions till ROI ends (marked by another
# `m5_exit instruction encountered`). We then start copying the output logs,
# present in the /home/gem5/spec2017/results directory to the `output_dir`.
# The runscript.sh file places `m5 exit` before and after the following command
# Therefore, we only pass this command without m5 exit.
command = "{} {} {}".format(args.benchmark, args.size, output_dir)
# For enabling CustomResource, we pass an additional parameter to mount the
# correct partition.
board.set_kernel_disk_workload(
# The x86 linux kernel will be automatically downloaded to the
# `~/.cache/gem5` directory if not already present.
# SPEC CPU2017 benchamarks were tested with kernel version 4.19.83
kernel=Resource(
"x86-linux-kernel-4.19.83",
),
# The location of the x86 SPEC CPU 2017 image
disk_image=CustomDiskImageResource(
args.image,
disk_root_partition=args.partition,
),
readfile_contents=command,
)
# We need this for long running processes.
m5.disableAllListeners()
root = Root(full_system = True, system = board)
# sim_quantum must be set when KVM cores are used.
root.sim_quantum = int(1e9)
m5.instantiate()
# We maintain the wall clock time.
globalStart = time.time()
print("Running the simulation")
print("Using atomic then timing cpu")
start_tick = m5.curTick()
end_tick = m5.curTick()
m5.stats.reset()
exit_event = m5.simulate()
if exit_event.getCause() == "m5_exit instruction encountered":
# We have completed booting the OS using KVM cpu
# Reached the start of ROI
print("Done booting Linux")
print("Resetting stats at the start of ROI!")
m5.stats.reset()
start_tick = m5.curTick()
# We switch to timing cpu for detailed simulation.
processor.switch()
else:
print("Unexpected termination of simulation before ROI was reached!")
print(
"Exiting @ tick {} because {}.".format(
m5.curTick(),
exit_event.getCause()
)
)
exit(-1)
# Simulate the ROI
exit_event = m5.simulate()
# Reached the end of ROI
gem5stats = get_simstat(root)
# We get the number of committed instructions from the timing
# cores. We then sum and print them at the end.
roi_insts = float(\
json.loads(gem5stats.dumps())\
["system"]["processor"]["cores2"]["core"]["exec_context.thread_0"]\
["numInsts"]["value"]
) + float(\
json.loads(gem5stats.dumps())\
["system"]["processor"]["cores3"]["core"]["exec_context.thread_0"]\
["numInsts"]["value"]\
)
if exit_event.getCause() == "m5_exit instruction encountered":
print("Dump stats at the end of the ROI!")
m5.stats.dump()
end_tick = m5.curTick()
m5.stats.reset()
else:
print("Unexpected termination of simulation while ROI was being executed!")
print(
"Exiting @ tick {} because {}.".format(
m5.curTick(),
exit_event.getCause()
)
)
exit(-1)
# We need to copy back the contents of the `speclogs' directory to
# m5.options.outdir
exit_event = m5.simulate()
if exit_event.getCause() == "m5_exit instruction encountered":
print("Output logs copied!")
else:
print("Unexpected termination of simulation while copying speclogs!")
print(
"Exiting @ tick {} because {}.".format(
m5.curTick(),
exit_event.getCause()
)
)
exit(-1)
print("Done with the simulation")
print()
print("Performance statistics:")
print("Simulated time in ROI: %.2fs" % ((end_tick-start_tick)/1e12))
print("Instructions executed in ROI: %d" % ((roi_insts)))
print("Ran a total of", m5.curTick()/1e12, "simulated seconds")
print("Total wallclock time: %.2fs, %.2f min" % \
(time.time()-globalStart, (time.time()-globalStart)/60))
多谢陌生人的指点。
版权声明:本文为hit_shaoqi原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。