【实验目的】
在多道程序或多任务系统中,系统同时处于就绪态的进程有若干个。也就是说能运行的进程数远远大于处理及个数。为了使系统中的各进程能有条不紊的运行,必须选择某种调度策略,以选择一进程占用处理机。要求学生设计一模拟单处理机调度的算法,以巩固和加深处理机调度的概念。
【实验原理】
- FCFS 即 first come first service,先来先服务调度算法,系统按照作业到达的先后次序来进行调度,或者说它优先考虑在系统中等待时间最长的作业,而不管该作业所需执行时间的长短,从后备作业队列中选择几个最先进入该队列的作业,将它们调入内存,为它们分配资源和创建进程。然后把它放入就绪队列。
- PSA 即 Priority-scheduling Algorithm,优先级调度算法,给每个作业一个优先级,优先级越高越先执行。
- RR 即 Round-Robin,时间片轮转算法,系统将所有的进程按FCFS策略排成一个就绪队列。系统可设置每隔一定时间便产生一次中断,把CPU分配给队首进程,使其执行一个时间片后,再把处理机分配给新的队首进程执行一个时间片,这样可使就绪队列中所有进程都可以再确定的时间片内获得一个时间片的处理机时间。
【实验内容及运行结果】
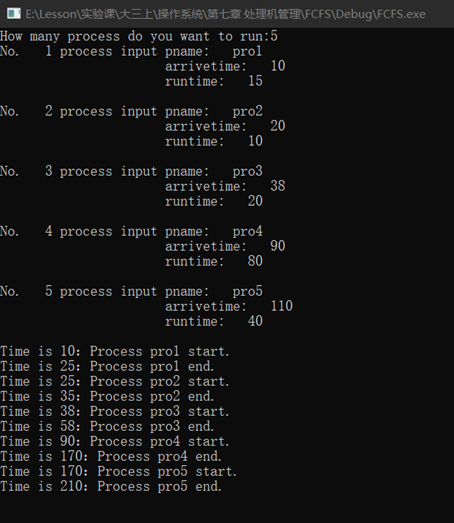
- 设计一个按先来先服务调度的算法
FCFS.cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <string.h>
struct PCB
{
char pname[10]; //进程名
int runtime; //估计运行时间
int arrivetime;//进程到达时间
int usetime; //进程已经占用CPU的时间
int needtime; //进程还需要运行的时间
char state; //进程状态。运行E、就绪R和完成F,初始状态为就绪状态
struct PCB* next;//进程队列指针
};
int time;//用于进程到达时间和需要时间
char strPname[10];
int num;
static char E = 'E', R = 'R', C = 'C';
struct PCB *p, *Head;
int totalTime = 0;
int main()
{
struct PCB *temp, *newPcb;
printf("How many process do you want to run:");
scanf("%d", &num);
p = (PCB*)malloc(sizeof(PCB));
Head = (PCB*)malloc(sizeof(PCB));
p = NULL;
Head = p;
temp = (PCB*)malloc(sizeof(PCB));
temp = Head;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
Head = p;
temp = Head;
newPcb = (PCB*)malloc(sizeof(PCB));
printf("No. %3d process input pname: ", i + 1);//提示输入进程名
scanf("%s", strPname);
strcpy(newPcb->pname, strPname);
printf(" arrivetime: ");//提示输入进程到达时间
scanf("%d", &time);
newPcb->arrivetime = time;
printf(" runtime: ");//提示输入进程运行时间
scanf("%d", &time);
printf("\n");
newPcb->runtime = time;
newPcb->state = 'R';
newPcb->next = NULL;
if (i == 0)
{
p = newPcb;
Head = p;
}
else if (i == 1)
{
if (p->arrivetime <= newPcb->arrivetime)
{
Head->next = newPcb;
}
else
{
newPcb->next = Head;
p = newPcb;
}
}
else
{
for (Head = p; Head != NULL; Head = Head->next)
{
temp = Head;
if (p->arrivetime > newPcb->arrivetime)
{
newPcb->next = Head;
p = newPcb;
break;
}
else if (Head->arrivetime <= newPcb->arrivetime &&Head->next != NULL && Head->next->arrivetime > newPcb->arrivetime)//注意后面两个的顺序,如果顺序调换会发生错误
{
newPcb->next = Head->next;
temp->next = newPcb;
break;
}
else if (Head->next == NULL)
{
temp->next = newPcb;
break;
}
}
}
}
int startTime = 0;//用于记录一个进程开始运行的时间
Head = p;
for (int i = 0; Head != NULL; i++)
{
if (Head->arrivetime <= i && Head->state == 'R')
{
startTime = i;//记录开始时间i为astartTime
Head->state = 'E';//进程为执行状态
printf("Time is %d:", i);
printf("Process %s start. \n", Head->pname);
}
else if (i - startTime == Head->runtime&&Head->state == 'E')
{
Head->state = 'F';
printf("Time is %d:", i);
printf("Process %s end. \n", Head->pname);
Head = Head->next;
i--;//这个很重要,主要在结束时刻是否有进程执行
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
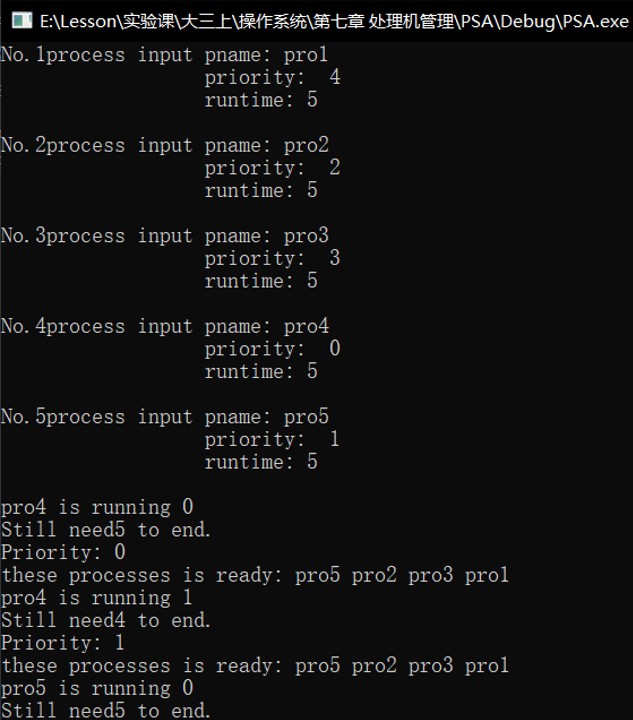
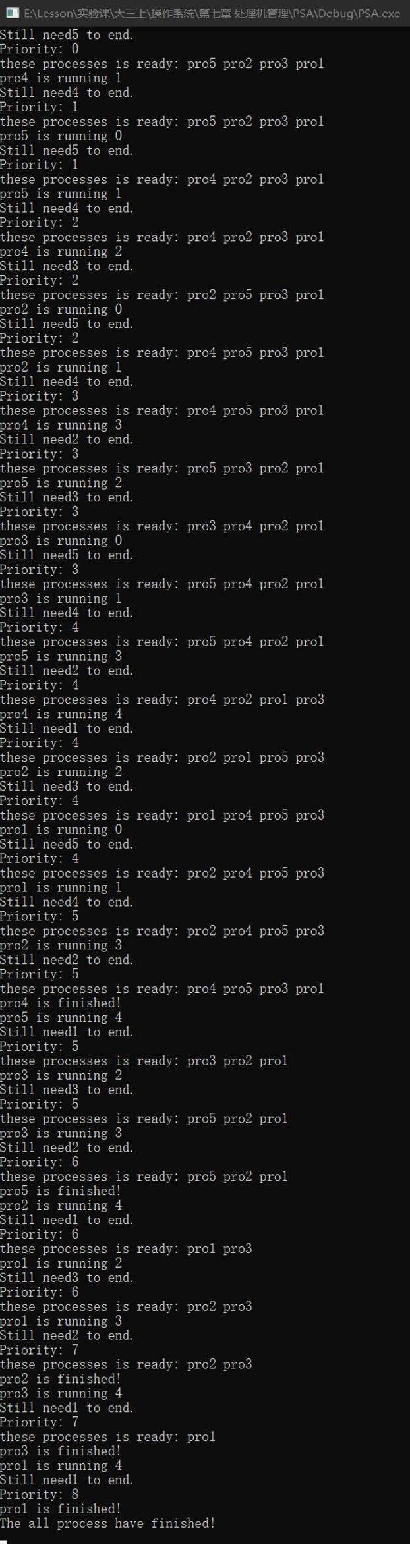
- 设计一个按优先级调度的算法
PSA.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<iomanip>
#include<algorithm>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int static now=0;
class PCB
{
public:
string pname; //进程名
int runtime; //估计需要时间
int ppriority; //优先级
int usetime; //已运行时间
char state; //进程状态
PCB *p;
};
bool cmp(PCB a, PCB b)
{
return a.ppriority<b.ppriority;
}
void run(PCB *head, PCB* running_process, int &pcount)
{
cout << running_process->pname << " is running " << running_process->usetime << endl;
cout << "Still need" << running_process->runtime<<" to end."<< endl;
cout<<"Priority: "<<running_process->ppriority<<endl;
running_process->runtime--;
running_process->ppriority++;
now++;
running_process->usetime++;
int temp=0;
if(pcount>1)
{
cout<<"these processes is ready: ";
for(int i=1; i<pcount; i++)
cout<<head[i].pname<<" ";
cout<<endl;
sort(head, head+pcount, cmp);
for(int i=1; i<pcount; i++)
{
head[i-1].p=&head[i];
}
running_process=head;
}
if(running_process->runtime==0)
{
running_process->state='C';
cout<<running_process->pname<<" is finished!"<<endl;
pcount--;
if(pcount!=0)
{
head=head->p;
running_process=head;
run(head, running_process, pcount);
}
else
cout<<"The all process have finished!"<<endl;
}
else
run(head, running_process, pcount);
}
int main()
{
PCB* head=new PCB();
head=NULL;
PCB* running_process=new PCB();
running_process=NULL;
int pcount=0;
PCB P[5];
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout<< "No."<< i + 1 <<"process input pname: ";
cin>>P[i].pname;
cout<<" priority: ";
cin>>P[i].ppriority;
cout<<" runtime: ";
cin>>P[i].runtime;
cout<<endl;
P[i].state='R';
P[i].p=NULL;
P[i].usetime=0;
pcount++;
}
sort(P, P+pcount, cmp);
head=&P[0];
running_process=&P[0];
for(int i=1; i<pcount; i++)
{
P[i-1].p=&P[i];
}
run(head, running_process, pcount);
while (1);
return 0;
}
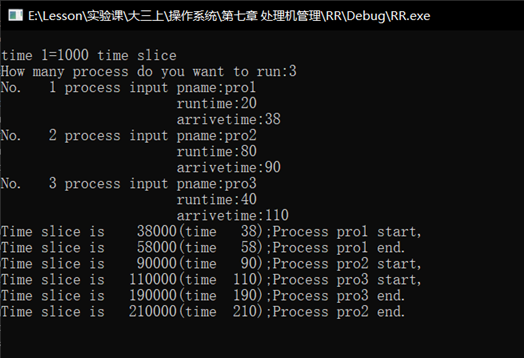
- 设计一个按时间片轮转法调度的算法
RR.cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct pcb {
char pname[50]; // 进程名
char state; // 进程状态
int runtime; // 估计运行时间
int arrivetime; // 到达时间
struct pcb* next; // 链接指针
}PCB;
PCB head_input; // 就绪队列队首
PCB head_run; // 当前运行进程
PCB* pcb_input;
static char R = 'r', C = 'c'; // R表示执行,C表示阻塞
unsigned long current; // 记录系统当前时间
void inputprocess(); // 建立进程函数
int readyprocess(); // 建立就绪队列函数
int readydata(); // 判断进程是否就绪函数
int runprocess(); // 运行进程函数
FILE* f;
// 定义就绪队列函数
int readyprocess() {
while (1) {
if (readydata() == 0) // 判断是否就绪函数
return 1;
else
runprocess(); // 运行进程函数
}
}
// 定义判断就绪队列是否有进程函数
int readydata() {
if (head_input.next == NULL) { // 就绪队列仅有一个进程
if (head_run.next == NULL) // 当前运行进程后为空
return 0;
else // 当前运行进城后非空
return 1;
}
PCB* p1, *p2, *p3;
p1 = head_run.next; // 当前运行进程后一个进程
p2 = &head_run; // 当前运行进程
while (p1 != NULL) { // 当前运行进程后非空
p2 = p1; // 运行下一个进程
p1 = p2->next;
}
p1 = p2;
p3 = head_input.next; // 就绪队列队首后一个进程
p2 = &head_input; // 就绪队列队首
while (p3 != NULL) {
if (((unsigned long)p3->arrivetime <= current) && (p3->state == R)) {
printf("Time slice is %8d(time %4d);Process %s start,\n",
current, (current + 500) / 1000, p3->pname);
fprintf(f, "Time slice is %8d(time %4d);Process %s start,\n",
current, (current + 500) / 1000, p3->pname);
p2->next = p3->next;
p3->next = p1->next;
p1->next = p3;
p3 = p2;
}
p2 = p3;
p3 = p3->next;
}
return 1;
}
// 定义运行进程函数
int runprocess() {
PCB* p1, *p2;
if (head_run.next == NULL) {
current++;
return 1;
}
else {
p1 = head_run.next;
p2 = &head_run;
while (p1 != NULL) {
p1->runtime--;
current++;
if (p1->runtime <= 0) {
printf("Time slice is %8d(time %4d);Process %s end. \n", current, (current + 500) / 1000,
p1->pname);
fprintf(f, "Time slice is %8d(time %4d);Process %s end. \n", current, (current + 500) / 1000,
p1->pname);
p1->state = C;
p2->next = p1->next;
delete p1;
p1 = NULL;
}
else {
p2 = p1;
p1 = p2->next;
}
}
return 1;
}
}
void inputprocess() {
PCB* p1, *p2;
int num;
unsigned long max = 0;
printf("How many process do you want to run:");
fprintf(f, "How many process do you want to run:");
scanf("%d", &num);
fprintf(f, "%d\n", &num);
p1 = &head_input;
p2 = p1;
p1->next = new PCB;
p1 = p1->next;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
printf("No. %3d process input pname:", i + 1);
fprintf(f, "No. %3d process input pname:", i + 1);
scanf("%s", p1->pname);
fprintf(f, "%s\n", p1->pname);
printf(" runtime:");
fprintf(f, " runtime:");
scanf("%d", &(p1->runtime));
fprintf(f, "%d\n", &(p1->runtime));
printf(" arrivetime:");
fprintf(f, " arrivetime:");
scanf("%d", &(p1->arrivetime));
fprintf(f, "%d\n", &(p1->arrivetime));
p1->runtime = (p1->runtime) * 1000;
p1->arrivetime = (p1->arrivetime) * 1000;
p1->state = R;
if ((unsigned long)(p1->arrivetime) > max)
max = p1->arrivetime;
p1->next = new PCB;
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
delete p1;
p1 = NULL;
p2->next = NULL;
}
// 定义建立进程函数
void inputprocess1() {
PCB* p1, *p2;
int num;
unsigned long max = 0;
printf("How many process do you want to run:");
fprintf(f, "How many process do you want to run:");
scanf("%d", &num);
fprintf(f, "%d\n", &num);
pcb_input = new PCB;
p1 = pcb_input;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
printf("No. %3d process input pname:", i + 1);
fprintf(f, "No. %3d process input pname:", i + 1);
scanf("%s", p1->pname);
printf(" runtime:");
fprintf(f, " runtime:");
scanf("%d", &(p1->runtime));
fprintf(f, "%d\n", &(p1->runtime));
printf(" arrivetime:");
fprintf(f, " arrivetime:");
scanf("%d", &(p1->arrivetime));
fprintf(f, "%d\n", &(p1->arrivetime));
//p1->runtime = (p1->runtime);
//p1->arrivetime = (p1->arrivetime);
p1->runtime = (p1->runtime) * 1000;
p1->arrivetime = (p1->arrivetime) * 1000;
p1->state = R;
if (i != num - 1) {
p1->next = new PCB;
p1 = p1->next;
}
else {
p1->next = pcb_input;
}
}
p1 = pcb_input;
while (p1->next != pcb_input) {
printf("process name is %s\n", p1->pname);
fprintf(f, "process name is %s\n", p1->pname);
p1 = p1->next;
}
printf("process name is %s\n", p1->pname);
fprintf(f, "process name is %s\n", p1->pname);
}
// 定义运行进程函数
void runprocess1() {
pcb* pre, *cur;
if (pcb_input == NULL)
return;
else {
cur = pcb_input;
pre = cur->next;
while (pre->next != cur) { // find the last node in the list
pre = pre->next;
}
while ((cur->runtime >= 0) || (cur->next != cur)) {
if (current < (unsigned long)cur->arrivetime) {
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
else {
if (current == (unsigned long)cur->arrivetime) {
printf("Time slice is %8d(time %4d);Process %s end. \n", current, (current + 500) / 1000,
cur->pname);
fprintf(f, "Time slice is %8d(time %4d);Process %s end. \n", current, (current + 500) / 1000,
cur->pname);
}
cur->runtime--;
if (cur->runtime < 0) {
printf("Time slice is %8d(time %4d);Process %s end. \n", current, (current + 500) / 1000,
cur->pname);
fprintf(f, "Time slice is %8d(time %4d);Process %s end. \n", current, (current + 500) / 1000,
cur->pname);
if (cur == cur->next) {
delete cur;
cur = NULL;
//break;
return;
}
else {
pre->next = cur->next;
pcb* tmp = cur;
delete tmp;
cur = pre->next;
}
}
else {
cur->runtime--;
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
current++;
}
}
}
// TO DO
int main() {
f = fopen("result.txt", "w");
printf("\ntime 1=1000 time slice\n");
fprintf(f, "\ntime 1=1000 time slice\n");
current = 0;
inputprocess();
readyprocess();
//inputprocess1();
//runprocess1();
_getch();
fclose(f);
return 0;
}
版权声明:本文为LeopoldZhang2000原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。