来看一段ThreadLocal的用法:
ThreadLocal<String>threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
},"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
threadLocal.set("aa");
},"t2");
t2.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
t1.start();
运行结果:null
我们来仔细分析一下:
threadLocal.set("aa");
第一次进入map为null,那么就创建一个
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
休眠5S后线程t1获取数据:
t1第一次进来就会初始化:
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
t1线程也是null,就会创建一个新的
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
最终内存布局图:
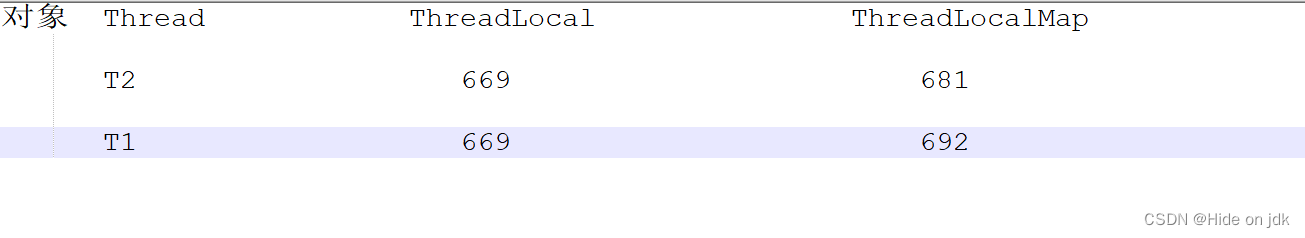
修改T2线程的代码:让其获取到值
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
threadLocal.set("aa");
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
},"t2");
第一次get的时候,map不为null,可以直接获取到值
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
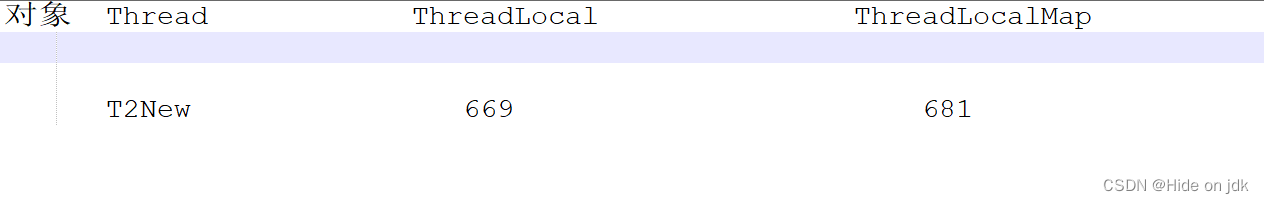
说到底:每一个线程进行set的时候,第一次进行get的时候为null,这时候就会创建一个新的
ThreadLocalMap,所以每个线程的ThreadLocalMap都是不同的。然后获取的时候,就会首先获取到自己的ThreadLocalMap,只要有set操作ThreadLocalMap就不会为null.
一句话总结:threadlocal就是保证每个线程有自己的独立副本。
版权声明:本文为u012222011原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。