一、cron表达式
语法:秒 分 时 日 月 周 年(Spring 不支持)
官方网站:http://www.quartz-scheduler.org/documentation/quartz-2.3.0/tutorials/crontrigger.html

特殊字符:
,:枚举;
(cron=“7,9,23 * * * * ?”):任意时刻的 7,9,23 秒启动这个任务;
-:范围:
(cron=“7-20 * * * * ?”):任意时刻的 7-20 秒之间,每秒启动一次
*:任意;
指定位置的任意时刻都可以
/:步长;
(cron=“7/5 * * * * ?”):第 7 秒启动,每 5 秒一次;
(cron=”*/5 * * * * ?”):任意秒启动,每 5 秒一次;
斜杠前面的是启动时间点,后边的是步长。
如果没有斜杠表示步长为1s
?:(出现在日和周几的位置):为了防止日和周冲突,在周和日上如果要写通配符使
用?,一般情况只有一个问号
(cron=”* * * 1 * ?”):每月的 1 号,启动这个任务;
L:(出现在日和周的位置)”,
last:最后一个
(cron=”* * * ? * 3L”):每月的最后一个周二
W:
Work Day:工作日
(cron=”* * * W * ?”):每个月的工作日触发
(cron=”* * * LW * ?”):每个月的最后一个工作日触发
#:第几个
(cron=”* * * ? * 5#2″):每个月的第 2 个周 4

二、SpringBoot 整合
注意:springboot中,支持6个参数,不支持年的选择,在设置第6个参数(周)时 用1-7分别代表周一到周日, 而原生cron表达式时1-7表示周日-周六。
2.1 基本使用
第一步:开启定时功能注解
@EnableScheduling
第二步:在方法上标注定时
@Scheduled
第三步:测试
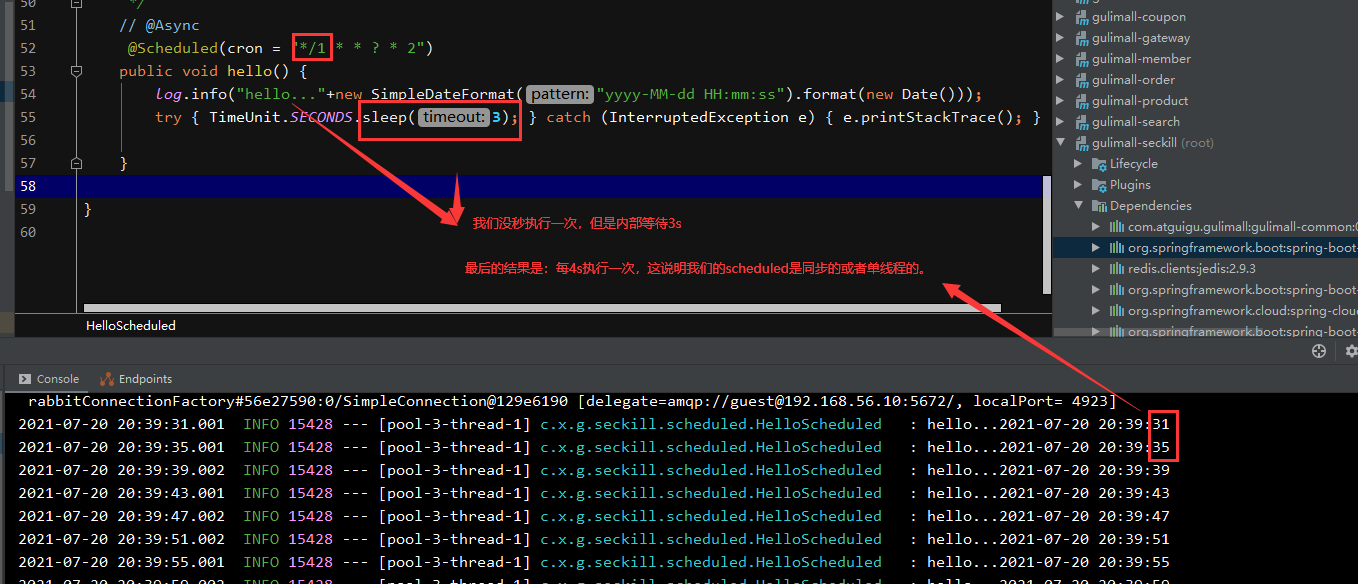
@Scheduled(cron = "*/1 * * ? * 2")
public void hello() {
log.info("hello..."+new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
2.2 异步任务
我们可以设置 @Scheduled异步执行
方法一:在配置文件中配置(这种放在某些boot版本不起作用,所以不推荐)
spring.task.scheduling.pool.size=10
方法二:★异步任务
第一步:开启异步任务
@EnableAsync
@EnableScheduling
@EnableAsync
@EnableScheduling
@Configuration
public class ScheduledConfig {
}
在方法上加上异步注解
@Async
@Async
@Scheduled(cron = "*/1 * * ? * 2")
public void hello() {
log.info("hello..."+new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
第二步:配置线程池
#异步任务的线程池
spring.task.execution.pool.core-size=4
spring.task.execution.pool.max-size=50
第三步:测试
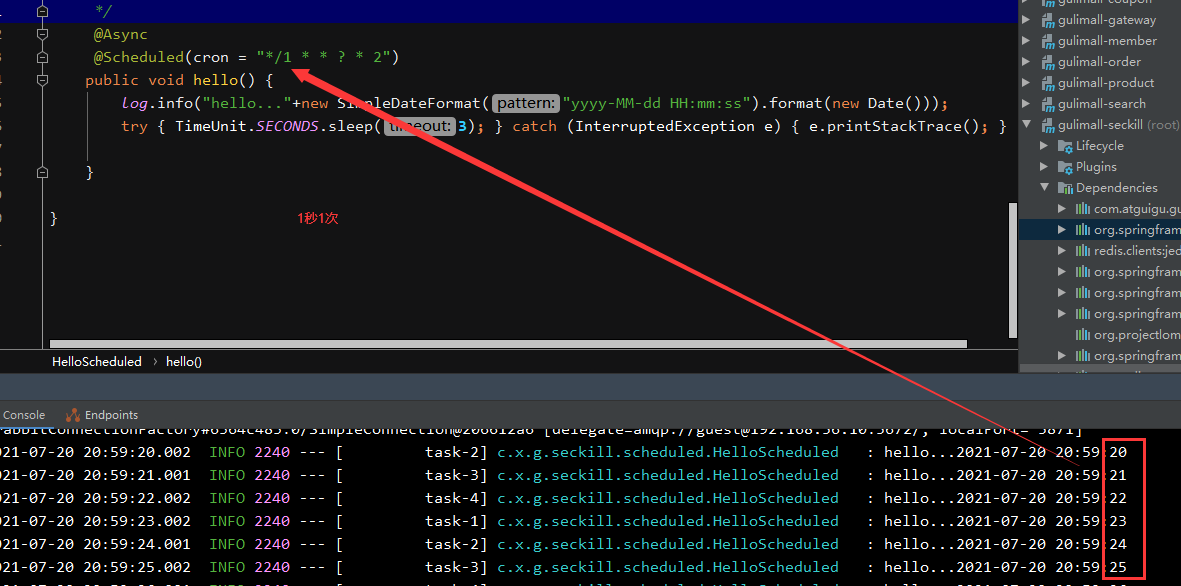
总结:
@EnableAsync + @Async 可以为任何方法创建异步任务。
三、★实战
通过Scheduling + 线程池+线程排列
3.1 背景
比如小区门口有个闸机,闸机会抓取车辆的出入记录保存到闸机服务器,一个闸机对应一个服务器,服务器提供了rest接口可以获取某一时间段的过车记录。一个小区可能有多个闸机。
我们的需求时要把小区的过车记录抓取保存到我们的平台上。
3.2 分析
首先抓起肯定不是一次性的,为了保证实时效果我们需要没5s请求一次闸机把数据获取到。但是一个小区有多个闸机如果我们用循环的方式一个一个获取,总时间就是所有闸机请求的和,(线程充足的情况下)如果用多线程就是最慢的那个闸机请求的时间。
3.3 代码过程
main方法用的springboot
@SpringBootApplication
public class ScheduledThreadApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ScheduledThreadApplication.class, args);
}
}
schedu任务,注意这几个配置
@Component 表示加入到ioc容器
@Configuration 表示时配置文件
@EnableAsync 开启异步,并不代表异步,要异步需要与@Async共同使用
@EnableScheduling 允许定时
@Slf4j
@Component
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
@EnableScheduling
public class ScheduleTask {
@Autowired
private Car car;
@Scheduled(cron = "*/2 * * ? * ?")
public void sendMqCarInAndCarOut1() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("★★★★★★--1111111111111111111-》" +Thread.currentThread() +"..." + new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
car.carInOut();
System.out.println("★★★★★★--1111111111111111111------------end-》" );
}
}
业务代码
@Component
public class Car {
/***
* 线程池----------start
*/
private static int corePoolSize = 10;
private static int maxPoolSize = 200;
private static int queueCapacity = 10;
static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
static {
executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
executor.initialize();
}
/***
* 线程池----------end
*/
// 4个业务线
private int count = 4;
public void carInOut() {
try {
// 把所有的任务放在集合中用于下面进行阻塞
CompletableFuture[] data = new CompletableFuture[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
CompletableFuture infoFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("★★★★★★---》" + Thread.currentThread() + "业务---"+new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
return null;
}, executor);
data[i] = infoFuture;
}
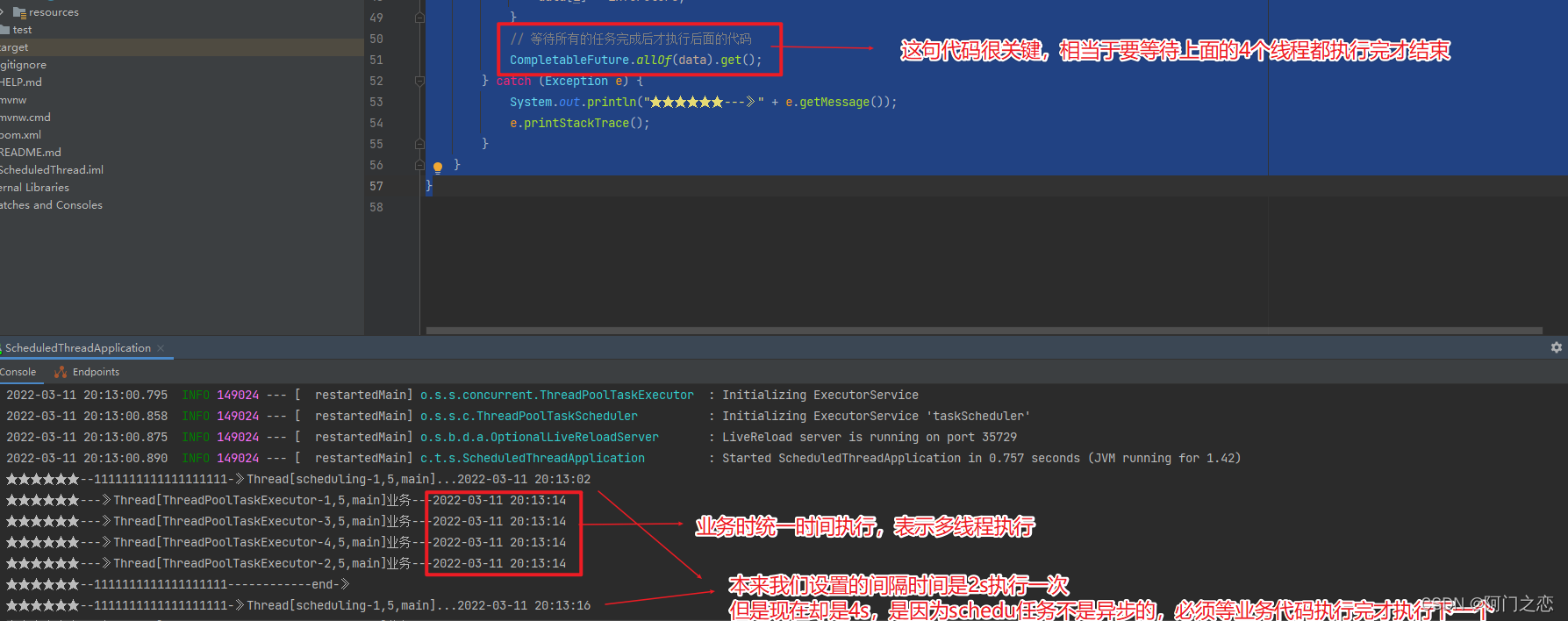
// 等待所有的任务完成后才执行后面的代码
CompletableFuture.allOf(data).get();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("★★★★★★---》" + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
最终效果