关注上方“Python数据科学”,选择星标,关键时间,第一时间送达!☞500g+超全学习资源免费领取

翻译:石头
来源:MachineLearningPlus
文末赠送5本书
《Python Web开发从入门到精通》
pandas是基于NumPy的一种数据分析工具,在机器学习任务中,我们首先需要对数据进行清洗和编辑等工作,pandas库大大简化了我们的工作量,熟练并掌握pandas常规用法是正确构建机器学习模型的第一步。
目录
1. 如何安装pandas
2. 如何导入pandas库和查询相应的版本信息
3. pandas数据类型
4. series教程
5. dataframe教程
6. 小结
1. 如何安装Pandas
最常用的方法是通过Anaconda安装,在终端或命令符输入如下命令安装:
conda install pandas若未安装Anaconda,使用Python自带的包管理工具pip来安装:
pip install pandas
2. 如何导入pandas库和查询相应的版本信息
import numpy as np # pandas和numpy常常结合在一起使用,导入numpy库import pandas as pd # 导入pandas库print(pd.__version__) # 打印pandas版本信息#> 0.23.4
3. pandas数据类型
pandas包含两种数据类型:series和dataframe。
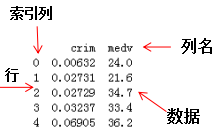
series是一种一维数据结构,每一个元素都带有一个索引,与一维数组的含义相似,其中索引可以为数字或字符串。series结构名称:

dataframe是一种二维数据结构,数据以表格形式(与excel类似)存储,有对应的行和列。dataframe结构名称:
4. series教程
1. 如何从列表,数组,字典构建series
mylist = list('abcedfghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz') # 列表
myarr = np.arange(26) # 数组
mydict = dict(zip(mylist, myarr)) # 字典# 构建方法
ser1 = pd.Series(mylist)
ser2 = pd.Series(myarr)
ser3 = pd.Series(mydict)print(ser3.head()) # 打印前5个数据#> a 0b 1c 2d 4e 3dtype:int642. 如何使series的索引列转化为dataframe的列
mylist = list('abcedfghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz')
myarr = np.arange(26)
mydict = dict(zip(mylist, myarr))
ser = pd.Series(mydict)# series转换为dataframe
df = ser.to_frame()# 索引列转换为dataframe的列
df.reset_index(inplace=True)print(df.head())#> index 00 a 01 b 12 c 23 e 34 d 43. 如何结合多个series组成dataframe
# 构建series1
ser1 = pd.Series(list('abcedfghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz')) # 构建series2
ser2 = pd.Series(np.arange(26))# 方法1,axis=1表示列拼接,0表示行拼接
df = pd.concat([ser1, ser2], axis=1)# 与方法1相比,方法2设置了列名
df = pd.DataFrame({'col1': ser1, 'col2': ser2})print(df.head())#> col1 col20 a 01 b 12 c 23 e 34 d 44. 如何命名列索引的名称
ser = pd.Series(list('abcedfghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'))# 命名索引列名称
ser.name = 'alphabets'# 显示前5行数据
ser.head()#> 0 a1 b2 c3 e4 d
Name: alphabets, dtype: object5. 如何获得series对象A中不包含series对象B的元素
ser1 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
ser2 = pd.Series([4, 5, 6, 7, 8])# 返回ser1不包含ser2的布尔型series
ser3=~ser1.isin(ser2)# 获取ser不包含ser2的元素
ser1[ser3]#> 0 11 22 3
dtype: int646. 如何获得seriesA和seriesB不相同的项
ser1 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
ser2 = pd.Series([4, 5, 6, 7, 8])# 求ser1和ser2的并集
ser_u = pd.Series(np.union1d(ser1, ser2))# 求ser1和ser2的交集
ser_i = pd.Series(np.intersect1d(ser1, ser2))# ser_i在ser_u的补集就是ser1和ser2不相同的项
ser_u[~ser_u.isin(ser_i)]#> 0 11 22 35 66 77 8
dtype: int647. 如何获得数值series的四分位值
# 设置随机数种子
state = np.random.RandomState(100)# 从均值为5标准差为25的正态分布随机抽取5个点构成series
ser = pd.Series(state.normal(10, 5, 25))# 求ser的四分位数
np.percentile(ser, q=[0, 25, 50, 75, 100])#> array([ 1.25117263, 7.70986507, 10.92259345, 13.36360403, 18.0949083 ])8. 如何获得series中单一项的频率计数
#从0~7随机抽取30个列表值,组成series
ser = pd.Series(np.take(list('abcdefgh'), np.random.randint(8, size=30)))# 对该series进行计数
ser.value_counts()#> d 8
g 6
b 6
a 5
e 2
h 2
f 1
dtype: int649. 如何保留series中前两个频次最多的项,其他项替换为‘other’
np.random.RandomState(100)# 从1~4均匀采样12个点组成series
ser = pd.Series(np.random.randint(1, 5, [12]))# 除前两行索引对应的值不变,后几行索引对应的值为Other
ser[~ser.isin(ser.value_counts().index[:2])] = 'Other'
ser#> 0 Other1 42 23 24 45 Other6 Other7 Other8 49 410 411 2
dtype: object 10. 如何对数值series分成10个相同数目的组
换个角度理解,对数值series离散化成10个类别(categorical)值
ser = pd.Series(np.random.random(20))# 离散化10个类别值,只显示前5行的数据
pd.qcut(ser, q=[0, .10, .20, .3, .4, .5, .6, .7, .8, .9, 1],
labels=['1st', '2nd', '3rd', '4th', '5th', '6th', '7th', '8th', '9th', '10th']).head()#>0 3rd1 1st2 6th3 6th4 9th
dtype: category
Categories (10, object): [1st < 2nd < 3rd < 4th ... 7th < 8th < 9th < 10th]11. 如何使numpy数组转化为给定形状的dataframe
ser = pd.Series(np.random.randint(1, 10, 35))# serier类型转换numpy类型,然后重构
df = pd.DataFrame(ser.values.reshape(7,5))print(df)#> 0 1 2 3 40 1 2 1 2 51 1 2 4 5 22 1 3 3 2 83 8 6 4 9 64 2 1 1 8 55 3 2 8 5 66 1 5 5 4 612. 如何找到series的值是3的倍数的位置
ser = pd.Series(np.random.randint(1, 10, 7))print(ser)# 获取值是3倍数的索引
np.argwhere(ser % 3==0)#> 0 61 82 63 74 65 26 4
dtype: int64#> array([[0],
[2],
[4]])13. 获取series中给定索引的元素(items)
ser = pd.Series(list('abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'))
index = [0, 4, 8, 14, 20]# 获取指定索引的元素
ser.take(index)#> 0 a4 e8 i14 o20 u
dtype: object14. 如何垂直和水平的拼接series
ser1 = pd.Series(range(5))
ser2 = pd.Series(list('abcde'))# 垂直拼接
df = pd.concat([ser1, ser2], axis=0)# 水平拼接
df = pd.concat([ser1, ser2], axis=1)print(df)#> 0 10 0 a1 1 b2 2 c3 3 d4 4 e15.如何获取series对象A中包含series对象B元素的位置
# ser1必须包含ser2,否则会报错
ser1 = pd.Series([10, 9, 6, 5, 3, 1, 12, 8, 13])
ser2 = pd.Series([1, 3, 10, 13])# 方法 1
[np.where(i == ser1)[0].tolist()[0] for i in ser2]# 方法 2
[pd.Index(ser1).get_loc(i) for i in ser2]#> [5, 4, 0, 8]16.如何计算series之间的均方差
truth = pd.Series(range(10))
pred = pd.Series(range(10)) + np.random.random(10)# 均方差
np.mean((truth-pred)**2)#> 0.2550872243419410317.如何使series中每个元素的首字母为大写
# series的元素为str类型
ser = pd.Series(['how', 'to', 'kick', 'ass?'])# 方法 1
ser.map(lambda x: x.title())# 方法 2 ,字符串相加
ser.map(lambda x: x[0].upper() + x[1:])# 方法 3
pd.Series([i.title() for i in ser])#> 0 How1 To2 Kick3 Ass?
dtype: object18.如何计算series中每个元素的字符串长度
ser = pd.Series(['how', 'to', 'kick', 'ass?'])# 方法
ser.map(lambda x: len(x))#> 0 31 22 43 4
dtype: int6419.如何计算series的一阶导和二阶导
ser = pd.Series([1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 27, 35])# 求一阶导并转化为列表类型print(ser.diff().tolist())# 求二阶导并转化为列表类型print(ser.diff().diff().tolist())#> [nan, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 6.0, 8.0]
[nan, nan, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 2.0]20.如何将一系列日期字符串转换为timeseries
ser = pd.Series(['01 Jan 2010', '02-02-2011', '20120303', '2013/04/04', '2014-05-05', '2015-06-06T12:20'])
pd.to_datetime(ser)#> 0 2010-01-01 00:00:001 2011-02-02 00:00:002 2012-03-03 00:00:003 2013-04-04 00:00:004 2014-05-05 00:00:005 2015-06-06 12:20:00
dtype: datetime64[ns]21. 如何从一个series中获取至少包含两个元音的元素
ser = pd.Series(['Apple', 'Orange', 'Plan', 'Python', 'Money'])# 方法from collections import Counter# Counter是一个类字典类型,键是元素值,值是元素出现的次数,满足条件的元素返回True
mask = ser.map(lambda x: sum([Counter(x.lower()).get(i, 0) for i in list('aeiou')]) >= 2)
ser[mask]#> 0 Apple1 Orange4 Money
dtype: object22. 如何计算根据另一个series分组后的series均值
fruit = pd.Series(np.random.choice(['apple', 'banana', 'carrot'], 10))
weights = pd.Series(np.linspace(1, 10, 10))# 根据fruit对weight分组
weightsGrouped = weights.groupby(fruit)print(weightsGrouped.indices)# 对分组后series求每个索引的平均值
weightsGrouped.mean()#> {'apple': array([0, 3], dtype=int64), 'banana': array([1, 2, 4, 8],
dtype=int64), 'carrot': array([5, 6, 7, 9], dtype=int64)}#> apple 2.50
banana 4.75
carrot 7.75
dtype: float6423. 如何计算两个series之间的欧氏距离
p = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
q = pd.Series([10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1])# 方法1sum((p - q)**2)**.5# 方法2
np.linalg.norm(p-q)#> 18.16590212458495 24. 如何在数值series中找局部最大值
局部最大值对应二阶导局部最小值
ser = pd.Series([2, 10, 3, 4, 9, 10, 2, 7, 3])# 二阶导
dd = np.diff(np.sign(np.diff(ser)))# 二阶导的最小值对应的值为最大值,返回最大值的索引
peak_locs = np.where(dd == -2)[0] + 1
peak_locs#> array([1, 5, 7], dtype=int64)25. 如何用最少出现的字符替换空格符
my_str = 'dbc deb abed gade'# 方法
ser = pd.Series(list('dbc deb abed gade'))# 统计元素的频数
freq = ser.value_counts()print(freq)# 求最小频数的字符
least_freq = freq.dropna().index[-1]# 替换"".join(ser.replace(' ', least_freq))#> d 43
b 3
e 3
a 2
c 1
g 1
dtype: int64#> 'dbcgdebgabedggade'26. 如何计算数值series的自相关系数
ser = pd.Series(np.arange(20) + np.random.normal(1, 10, 20))# 求series的自相关系数,i为偏移量
autocorrelations = [ser.autocorr(i).round(2) for i in range(11)]print(autocorrelations[1:])# 选择最大的偏移量print('Lag having highest correlation: ', np.argmax(np.abs(autocorrelations[1:]))+1)#> [0.33, 0.41, 0.48, 0.01, 0.21, 0.16, -0.11, 0.05, 0.34, -0.24]#> Lag having highest correlation: 327. 如何对series进行算术运算操作
# 如何对series之间进行算法运算import pandas as pd
series1 = pd.Series([3,4,4,4],['index1','index2','index3','index4'])
series2 = pd.Series([2,2,2,2],['index1','index2','index33','index44'])# 加法
series_add = series1 + series2print(series_add)# 减法
series_minus = series1 - series2# series_minus# 乘法
series_multi = series1 * series2# series_multi# 除法
series_div = series1/series2
series_divseries是基于索引进行算数运算操作的,pandas会根据索引对数据进行运算,若series之间有不同的索引,对应的值就为Nan。结果如下:
#加法:
index1 5.0
index2 6.0
index3 NaN
index33 NaN
index4 NaN
index44 NaN
dtype: float64#除法:
index1 1.5
index2 2.0
index3 NaN
index33 NaN
index4 NaN
index44 NaN
dtype: float64
3. dataframe教程
1. 如何从csv文件只读取前几行的数据
# 只读取前2行和指定列的数据
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/Cars93_miss.csv',nrows=2,usecols=['Model','Length'])
df#> Model Length0 Integra 1771 Legend 1952. 如何从csv文件中每隔n行来创建dataframe
# 每隔50行读取一行数据
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/BostonHousing.csv', chunksize=50)
df2 = pd.DataFrame()for chunk in df:# 获取series
df2 = df2.append(chunk.iloc[0,:])#显示前5行print(df2.head())#> crim zn indus chas nox rm age \0 0.21977 0.0 6.91 0 0.44799999999999995 5.602 62.0 1 0.0686 0.0 2.89 0 0.445 7.416 62.5 2 2.7339700000000002 0.0 19.58 0 0.871 5.597 94.9 3 0.0315 95.0 1.47 0 0.40299999999999997 6.975 15.3 4 0.19072999999999998 22.0 5.86 0 0.431 6.718 17.5
dis rad tax ptratio b lstat medv 0 6.0877 3 233 17.9 396.9 16.2 19.4 1 3.4952 2 276 18.0 396.9 6.19 33.2 2 1.5257 5 403 14.7 351.85 21.45 15.4 3 7.6534 3 402 17.0 396.9 4.56 34.9 4 7.8265 7 330 19.1 393.74 6.56 26.2 3. 如何改变导入csv文件的列值
改变列名‘medv’的值,当列值≤25时,赋值为‘Low’;列值>25时,赋值为‘High’.
# 使用converters参数,改变medv列的值
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/BostonHousing.csv',
converters={'medv': lambda x: 'High' if float(x) > 25 else 'Low'})print(df.head())#> b lstat medv0 396.90 4.98 Low 1 396.90 9.14 Low 2 392.83 4.03 High 3 394.63 2.94 High 4 396.90 5.33 High4. 如何从csv文件导入指定的列
# 导入指定的列:crim和medv
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/BostonHousing.csv', usecols=['crim', 'medv'])# 打印前四行dataframe信息print(df.head())#> crim medv0 0.00632 24.01 0.02731 21.62 0.02729 34.73 0.03237 33.44 0.06905 36.25. 如何得到dataframe的行,列,每一列的类型和相应的描述统计信息
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/Cars93_miss.csv')# 打印dataframe的行和列print(df.shape)# 打印dataframe每列元素的类型显示前5行print(df.dtypes.head())# 统计各类型的数目,方法1print(df.get_dtype_counts())# 统计各类型的数目,方法2# print(df.dtypes.value_counts())# 描述每列的统计信息,如std,四分位数等
df_stats = df.describe()# dataframe转化数组
df_arr = df.values# 数组转化为列表
df_list = df.values.tolist()#> (93, 27)
Manufacturer object
Model object
Type object
Min.Price float64
Price float64
dtype: object
float64 18object 9
dtype: int646. 如何获取给定条件的行和列
import numpy as np
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/Cars93_miss.csv')# print(df)# 获取最大值的行和列
row, col = np.where(df.values == np.max(df.Price))# 行和列获取最大值print(df.iat[row[0], col[0]])
df.iloc[row[0], col[0]]# 行索引和列名获取最大值
df.at[row[0], 'Price']
df.get_value(row[0], 'Price')#> 61.9 7. 如何重命名dataframe的特定列
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.array([[18,50],[19,51],[20,55]]),index=['man1','man2','man3'],columns=['age','weight'])print(df1)# 修改列名print("\nchange columns :\n")#方法1
df1.rename(columns={'weight':'stress'})#方法2
df1.columns.values[1] = 'stress'print(df1)#> age weight
man1 18 50
man2 19 51
man3 20 55
change columns :
age stress
man1 18 50
man2 19 51
man3 20 558. 如何检查dataframe中是否有缺失值
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/Cars93_miss.csv')# 若有缺失值,则为Ture
df.isnull().values.any()#> True9. 如何统计dataframe的每列中缺失值的个数
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/Cars93_miss.csv')# 获取每列的缺失值个数
n_missings_each_col = df.apply(lambda x: x.isnull().sum())print(n_missings_each_col.head())#> Manufacturer 4
Model 1
Type 3
Min.Price 7
Price 2
dtype: int6410. 如何用平均值替换相应列的缺失值
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/Cars93_miss.csv',nrows=10)print(df[['Min.Price','Max.Price']].head())# 平均值替换缺失值
df_out = df[['Min.Price', 'Max.Price']] = df[['Min.Price', 'Max.Price']].apply(lambda x: x.fillna(x.mean()))print(df_out.head())#> Min.Price Max.Price0 12.9 18.81 29.2 38.72 25.9 32.33 NaN 44.64 NaN NaN#> Min.Price Max.Price0 12.9 18.81 29.2 38.72 25.9 32.33 23.0 44.64 23.0 29.911. 如何用全局变量作为apply函数的附加参数处理指定的列
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/Cars93_miss.csv')print(df[['Min.Price', 'Max.Price']].head())# 全局变量
d = {'Min.Price': np.nanmean, 'Max.Price': np.nanmedian}# 列名Min.Price的缺失值用平均值代替,Max.Price的缺失值用中值代替
df[['Min.Price', 'Max.Price']] = df[['Min.Price', 'Max.Price']].apply(lambda x, d: x.fillna(d[x.name](x)), args=(d, ))print(df[['Min.Price', 'Max.Price']].head())#> Min.Price Max.Price0 12.9 18.81 29.2 38.72 25.9 32.33 NaN 44.64 NaN NaN#> Min.Price Max.Price0 12.900000 18.801 29.200000 38.702 25.900000 32.303 17.118605 44.604 17.118605 19.1512. 如何以dataframe的形式选择特定的列
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(-1, 5), columns=list('abcde'))# print(df)# 以dataframe的形式选择特定的列type(df[['a']])type(df.loc[:, ['a']])print(type(df.iloc[:, [0]]))# 以series的形式选择特定的列type(df.a)type(df['a'])type(df.loc[:, 'a'])print(type(df.iloc[:, 1]))#> <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>13. 如何改变dataframe中的列顺序
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(-1, 5), columns=list('abcde'))print(df)# 交换col1和col2def switch_columns(df, col1=None, col2=None):
colnames = df.columns.tolist()
i1, i2 = colnames.index(col1), colnames.index(col2)
colnames[i2], colnames[i1] = colnames[i1], colnames[i2]return df[colnames]
df1 = switch_columns(df, 'a', 'c')print(df1)#> a b c d e0 0 1 2 3 41 5 6 7 8 92 10 11 12 13 143 15 16 17 18 19#> c b a d e0 2 1 0 3 41 7 6 5 8 92 12 11 10 13 143 17 16 15 18 1914. 如何格式化dataframe的值
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random(4)**10, columns=['random'])print(df)# 显示小数点后四位
df.apply(lambda x: '%.4f' % x, axis=1)print(df)#> random0 3.539348e-041 3.864140e-102 2.973575e-023 1.414061e-01#> random0 3.539348e-041 3.864140e-102 2.973575e-023 1.414061e-0115. 如何将dataframe中的所有值以百分数的格式表示
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random(4), columns=['random'])# 格式化为小数点后两位的百分数
out = df.style.format({'random': '{0:.2%}'.format,
})
out#> random0 48.54%1 91.51%2 90.83%3 20.45%16.如何从dataframe中每隔n行构建dataframe
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/Cars93_miss.csv')# 每隔20行读dataframe数据print(df.iloc[::20, :][['Manufacturer', 'Model', 'Type']])#> Manufacturer Model Type0 Acura Integra Small20 Chrysler LeBaron Compact40 Honda Prelude Sporty60 Mercury Cougar Midsize80 Subaru Loyale Small17. 如何得到列中前n个最大值对应的索引
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1, 15, 15).reshape(5,-1), columns=list('abc'))print(df)# 取'a'列前3个最大值对应的行
n = 5
df['a'].argsort()[::-1].iloc[:3]#> a b c0 5 5 21 12 7 12 5 2 123 5 14 124 1 13 13#> 4 13 32 2
Name: a, dtype: int6418. 如何获得dataframe行的和大于100的最末n行索引
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(10, 40, 16).reshape(-1, 4))print(df)# dataframe每行的和
rowsums = df.apply(np.sum, axis=1)# 选取大于100的最末两行索引# last_two_rows = df.iloc[np.where(rowsums > 100)[0][-2:], :]
nline = np.where(rowsums > 100)[0][-2:]
nline#> 0 1 2 30 19 34 15 121 38 35 14 262 39 32 18 203 28 27 36 38#> array([2, 3], dtype=int64)19. 如何从series中查找异常值并赋值
ser = pd.Series(np.logspace(-2, 2, 30))# 小于low_per分位的数赋值为low,大于low_per分位的数赋值为highdef cap_outliers(ser, low_perc, high_perc):
low, high = ser.quantile([low_perc, high_perc])print(low_perc, '%ile: ', low, '|', high_perc, '%ile: ', high)
ser[ser < low] = low
ser[ser > high] = highreturn(ser)
capped_ser = cap_outliers(ser, .05, .95)#> 0.05 %ile: 0.016049294076965887 | 0.95 %ile: 63.87667222018393420. 如何交换dataframe的两行
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3, -1))print(df)# 函数def swap_rows(df, i1, i2):
a, b = df.iloc[i1, :].copy(), df.iloc[i2, :].copy()# 通过iloc换行
df.iloc[i1, :], df.iloc[i2, :] = b, areturn df# 2和3行互换print(swap_rows(df, 1, 2))#> 0 1 20 0 1 21 3 4 52 6 7 8#> 0 1 20 0 1 21 6 7 82 3 4 521. 如何倒转dataframe的行
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3, -1))print(df)# 方法 1
df.iloc[::-1, :]# 方法 2print(df.loc[df.index[::-1], :])#> 0 1 20 0 1 21 3 4 52 6 7 8#> 0 1 22 6 7 81 3 4 50 0 1 222. 如何对分类变量进行one-hot编码
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(25).reshape(5,-1), columns=list('abcde'))print(df)# 对列'a'进行onehot编码
df_onehot = pd.concat([pd.get_dummies(df['a']), df[list('bcde')]], axis=1)print(df_onehot)#> a b c d e0 0 1 2 3 41 5 6 7 8 92 10 11 12 13 143 15 16 17 18 194 20 21 22 23 24#> 0 5 10 15 20 b c d e0 1 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 41 0 1 0 0 0 6 7 8 92 0 0 1 0 0 11 12 13 143 0 0 0 1 0 16 17 18 194 0 0 0 0 1 21 22 23 2423. 如何获取dataframe行方向上最大值个数最多的列
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 9).reshape(3, -1))print(df)# 获取每列包含行方向上最大值的个数
count_series = df.apply(np.argmax, axis=1).value_counts()print(count_series)# 输出行方向最大值个数最多的列的索引print('Column with highest row maxes: ', count_series.index[0])#> 0 1 20 46 31 341 38 13 62 1 18 15#>统计列的最大值的个数0 21 1
dtype: int64#> Column with highest row maxes: 024. 如何得到列之间最大的相关系数
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 16).reshape(4, -1), columns=list('pqrs'), index=list('abcd'))# dfprint(df)# 得到四个列的相关系数
abs_corrmat = np.abs(df.corr())print(abs_corrmat)# 得到每个列名与其他列的最大相关系数
max_corr = abs_corrmat.apply(lambda x: sorted(x)[-2])# 显示每列与其他列的相关系数print('Maximum Correlation possible for each column: ', np.round(max_corr.tolist(), 2))#> p q r s
a 59 99 1 34
b 89 60 97 40
c 43 35 14 6
d 70 59 30 53#> p q r s
p 1.000000 0.200375 0.860051 0.744529
q 0.200375 1.000000 0.236619 0.438541
r 0.860051 0.236619 1.000000 0.341399
s 0.744529 0.438541 0.341399 1.000000#> Maximum Correlation possible for each column: [0.86 0.44 0.86 0.74]25. 如何创建包含每行最小值与最大值比例的列
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 9).reshape(3, -1))print(df)# 方法1:axis=1表示行方向,
min_by_max = df.apply(lambda x: np.min(x)/np.max(x), axis=1)# 方法2
min_by_max = np.min(df, axis=1)/np.max(df, axis=1)
min_by_max#> 0 1 20 81 68 591 45 73 232 20 22 69#> 0 0.7283951 0.3150682 0.289855
dtype: float6426. 如何创建包含每行第二大值的列
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 9).reshape(3, -1))print(df)# 行方向上取第二大的值组成series
out = df.apply(lambda x: x.sort_values().unique()[-2], axis=1)# 构建dataframe新的列
df['penultimate'] = outprint(df)#> 0 1 20 28 77 11 43 19 692 29 30 72#> 0 1 2 penultimate0 28 77 1 281 43 19 69 432 29 30 72 3027. 如何归一化dataframe的所有列
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 80).reshape(8, -1))# 正态分布归一化
out1 = df.apply(lambda x: ((x - x.mean())/x.std()).round(2))print('Solution Q1\n',out1)# 线性归一化
out2 = df.apply(lambda x: ((x.max() - x)/(x.max() - x.min())).round(2))print('Solution Q2\n', out2)28. 如何计算每一行与下一行的相关性
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 25).reshape(5, -1))# 行与行之间的相关性
[df.iloc[i].corr(df.iloc[i+1]).round(2) for i in range(df.shape[0])[:-1]]29. 如何用0赋值dataframe的主对角线和副对角线
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 25).reshape(5, -1))print(df)# zhufor i in range(df.shape[0]):
df.iat[i, i] = 0
df.iat[df.shape[0]-i-1, i] = 0print(df)#> 0 1 2 3 40 51 35 71 71 791 78 25 71 85 442 90 97 72 14 43 27 91 37 25 484 1 26 68 70 20#> 0 1 2 3 40 0 35 71 71 01 78 0 71 0 442 90 97 0 14 43 27 0 37 0 484 0 26 68 70 030.如何得到按列分组的dataframe的平均值和标准差
df = pd.DataFrame({'col1': ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] * 2,'col2': np.random.randint(0,15,6),'col3': np.random.randint(0, 15, 6)})print(df)# 按列col1分组后的平均值
df_grouped_mean = df.groupby(['col1']).mean()print(df_grouped_mean)# 按列col1分组后的标准差
df_grouped_std = df.groupby(['col1']).mean()print(df_grouped_std)#> col1 col2 col30 apple 2 141 banana 11 82 orange 8 103 apple 5 24 banana 6 125 orange 11 13#> col2 col3
col1
apple 3.5 8.0
banana 8.5 10.0
orange 9.5 11.5#> col2 col3
col1
apple 3.5 8.0
banana 8.5 10.0
orange 9.5 11.531. 如何得到按列分组后另一列的第n大的值
df = pd.DataFrame({'fruit': ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] * 2,'taste': np.random.rand(6),'price': np.random.randint(0, 15, 6)})print(df)# teste列按fruit分组
df_grpd = df['taste'].groupby(df.fruit)# teste列中banana元素的信息
x=df_grpd.get_group('banana')# 排序并找第2大的值
s = x.sort_values().iloc[-2]print(s)#> fruit taste price0 apple 0.521990 71 banana 0.640444 02 orange 0.460509 93 apple 0.818963 44 banana 0.646138 75 orange 0.917056 12#> 0.640443643608596732. 如何计算分组dataframe的平均值,并将分组列保留为另一列
df = pd.DataFrame({'fruit': ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] * 2,'rating': np.random.rand(6),'price': np.random.randint(0, 15, 6)})# 按fruit分组后,price列的平均值,并将分组置为一列
out = df.groupby('fruit', as_index=False)['price'].mean()print(out)#> fruit price0 apple 4.01 banana 6.52 orange 11.033.如何获取两列值元素相等的位置(并非索引)
df = pd.DataFrame({'fruit1': np.random.choice(['apple', 'orange', 'banana'], 3),'fruit2': np.random.choice(['apple', 'orange', 'banana'], 3)})print(df)# 获取两列元素相等的行
np.where(df.fruit1 == df.fruit2)#> fruit1 fruit20 apple banana1 apple apple2 orange apple#> (array([1], dtype=int64),)34. 如何创建指定列偏移后的新列
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1, 100, 20).reshape(-1, 4), columns = list('abcd'))# 创建往下偏移后的列
df['a_lag1'] = df['a'].shift(1)# 创建往上偏移后的列
df['b_lead1'] = df['b'].shift(-1)print(df)#> a b c d a_lag1 b_lead10 29 90 43 24 NaN 36.01 94 36 67 66 29.0 76.02 81 76 44 49 94.0 97.03 55 97 10 74 81.0 43.04 32 43 62 62 55.0 NaN35. 如何获得dataframe中单一值的频数
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1, 10, 20).reshape(-1, 4), columns = list('abcd'))# 统计元素值的个数
pd.value_counts(df.values.ravel())#> 9 37 33 31 36 25 24 28 12 1
dtype: int6436. 如何将文本拆分为两个单独的列
df = pd.DataFrame(["STD, City State","33, Kolkata West Bengal","44, Chennai Tamil Nadu","40, Hyderabad Telengana","80, Bangalore Karnataka"], columns=['row'])print(df)# expand=True表示以分割符把字符串分成两列
df_out = df.row.str.split(',|\t', expand=True)# 获取新的列
new_header = df_out.iloc[0]# 重新赋值
df_out = df_out[1:]
df_out.columns = new_headerprint(df_out)#> row0 STD, City State1 33, Kolkata West Bengal2 44, Chennai Tamil Nadu3 40, Hyderabad Telengana4 80, Bangalore Karnataka#> 0 STD City State1 33 Kolkata West Bengal2 44 Chennai Tamil Nadu3 40 Hyderabad Telengana4 80 Bangalore Karnataka 37.如何构建多级索引的dataframe
我们利用元组(Tuple)构建多级索引,然后定义dataframe.
# 如何构建多级索引的dataframe# 先通过元组方式构建多级索引import numpy as np
outside = ['A','A','A','B','B','B']
inside =[1,2,3,1,2,3]
my_index = list(zip(outside,inside))# my_index# 转化为pd格式的索引
my_index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples(my_index)# my_index# 构建多级索引dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(6,2),index =my_index,columns=['fea1','fea2'])
df 多索引dataframe结果:
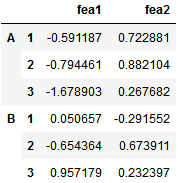
获取多索引dataframe的数据:
df.loc['A'].iloc[1]#> fea1 -0.794461
fea2 0.882104
Name: 2, dtype: float64
df.loc['A'].iloc[1]['fea1']#> -0.7944609970323794
六、小结
pandas库在机器学习项目中的应用主要有两个步骤:(1)读取文件,(2)数据清洗和编辑工作,该步骤中,我们常常需要借组numpy数组来处理数据。希望这篇文章能够让你很好的入门pandas库,多多练习才是王道 。读者能够看到这里的都是真爱,点个在看和广告呗!
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42156420/article/details/82813482
文末赠书福利
赠送新出的书籍《Python Web开发从入门到精通》5本!由「北京大学出版社」赞助提供,如果等不及也可以入手一本学习。
介绍:
本书分为3部分:第1部分是基础篇,带领初学者实践Python开发环境和掌握基本语法,同时对网络协议、Web客户端技术、数据库建模编程等网络编程基础深入浅出地进行学习;第2部分是框架篇,学习当前*流行的Python Web框架,即Django、Tornado、Flask和Twisted,达到对各种Python网络技术融会贯通的目的;第3部分是实战篇,分别对几种常用WEB框架进行项目实践,利用其各自的特点开发适用于不同场景的网络程序。
参与方式:本篇文章
底部
「
点赞
」
+
「
在看
」+
「
留言
」,文章内容相关的优质留言才可上墙!留言点赞数量最多
前5位
读者将获得这本书,
截止时间「
11月14日20:00
」
,最终获赠者通过留言联系我。
推荐阅读安利3个Python数据分析EDA神器!骚操作!嵌套 JSON 秒变 Dataframe!计算机专业几本必看的书!太强了!一款如操作Excel一样的pandas可视化神器来了!两篇毕业论文致谢同一个女朋友?哈哈哈哈!太震撼了!我用Python画出全北京的公交线路动图学习Anaconda一定要了解这几件事
🧐
分享、点赞、在看
,给个
三连击
呗!
👇