坐标旋转
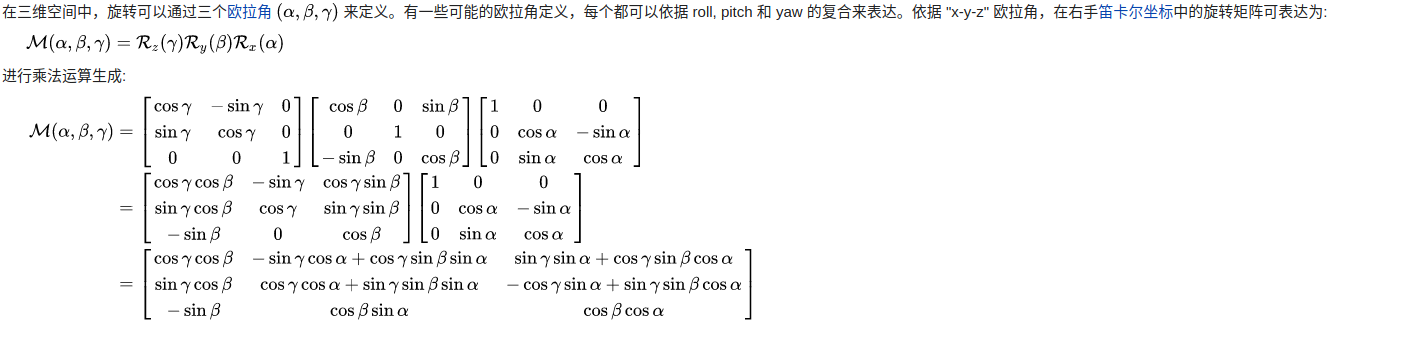
坐标旋转包含绕x、y、z轴旋转,在右手坐标系中,x-翻滚(roll),y-俯仰(pitch),z-航向(yaw),详细可参考维基百科。自动驾驶中,还需要将车体坐标系转换到大地坐标系,此时还需要当前车体的位置、姿态。
从baseLink到map的转换关系为:先绕x轴旋转,在绕y轴旋转,最后绕z轴旋转,即左乘为Rzyx, 然后在平移t. 从map到baseLink的转换关系正好相反,先平移-t, 然后绕z轴旋转,在绕y轴,最后绕x轴. 注意,此时旋转的角度与baseLink到map的正好相反.
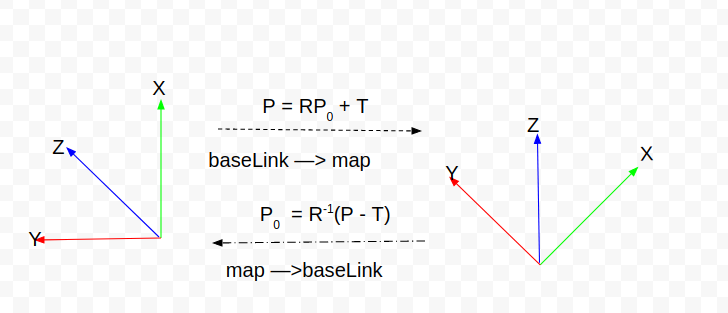
已知当前车体坐标系的点云cloud,当前车体的位置即姿态x, y, z, roll, pitch, yaw。通过pcl::getTransformation获取从车体坐标系到大地坐标系的旋转矩阵。
Eigen::Affine3f transCur = pcl::getTransformation(x, y, z, roll, pitch, yaw);
其中getTransformation的计算过程如下,先计算旋转,在加上平移量x, y, z:计算过程如下
Eigen::Matrix3f getRomateZYXMat(float yaw, float pitch, float roll){
float cz = cos(yaw);
float sz = sin(yaw);
float cx = cos(roll);
float sx = sin(roll);
float cy = cos(pitch);
float sy = sin(pitch);
Eigen::Matrix3f Rx, Ry, Rz, mat;
Rx << 1, 0, 0,
0, cx, -sx,
0, sx, cx;
Ry << cy, 0, sy,
0, 1, 0,
-sy, 0, cy;
Rz << cz, -sz, 0,
sz, cz, 0,
0 , 0, 1;
mat = Rx * Ry * Rz;
return mat;
}
pcl中中的计算方式,二者的结果是一样的.
template <typename Scalar> void
pcl::getTransformation (Scalar x, Scalar y, Scalar z,
Scalar roll, Scalar pitch, Scalar yaw,
Eigen::Transform<Scalar, 3, Eigen::Affine> &t)
{
Scalar A = cos (yaw), B = sin (yaw), C = cos (pitch), D = sin (pitch),
E = cos (roll), F = sin (roll), DE = D*E, DF = D*F;
t (0, 0) = A*C; t (0, 1) = A*DF - B*E; t (0, 2) = B*F + A*DE; t (0, 3) = x;
t (1, 0) = B*C; t (1, 1) = A*E + B*DF; t (1, 2) = B*DE - A*F; t (1, 3) = y;
t (2, 0) = -D; t (2, 1) = C*F; t (2, 2) = C*E; t (2, 3) = z;
t (3, 0) = 0; t (3, 1) = 0; t (3, 2) = 0; t (3, 3) = 1;
}
最后pcl::transformPointCloud将cloud转换到大地坐标系。
pcl::transformPointCloud(cloud, *colorPclPtr, transCur);
void se3 (const float* src, float* tgt) const
{
const Scalar p[3] = { src[0], src[1], src[2] };//车体坐标系的点
tgt[0] = static_cast<float> (tf (0, 0) * p[0] + tf (0, 1) * p[1] + tf (0, 2) * p[2] + tf (0, 3));
tgt[1] = static_cast<float> (tf (1, 0) * p[0] + tf (1, 1) * p[1] + tf (1, 2) * p[2] + tf (1, 3));
tgt[2] = static_cast<float> (tf (2, 0) * p[0] + tf (2, 1) * p[1] + tf (2, 2) * p[2] + tf (2, 3));
tgt[3] = 1;
}
如果大地坐标系下的点云想转换到车体坐标系,则需要先减去当前车体的坐标,然后在反方向旋转得到原始点云。
Eigen::Matrix3f getRomateXYZMat(float roll, float pitch, float yaw){
float cz = cos(yaw);
float sz = sin(yaw);
float cx = cos(roll);
float sx = sin(roll);
float cy = cos(pitch);
float sy = sin(pitch);
Eigen::Matrix3f Rx, Ry, Rz, mat;
Rx << 1, 0, 0,
0, cx, -sx,
0, sx, cx;
Ry << cy, 0, sy,
0, 1, 0,
-sy, 0, cy;
Rz << cz, -sz, 0,
sz, cz, 0,
0 , 0, 1;
mat = Rz * Ry * Rx;
return mat;
}
也可以按照前面的公式,求出旋转和平移的联合矩阵$\left [R^{-1} : R^{-1} * -T \right ] $。
//获取反向旋转矩阵
Eigen::Matrix3f transCurMap = getRomateZYXMat(-yaw, -pitch, -roll);
//平移向量
Eigen::MatrixXf t0(3,1);
t0<<-x, -y, -z;
Eigen::MatrixXf transMat(3, 1);
transMat = transCurMap.matrix() * t0;
最后,如果通过TF获取base_link和map的坐标转换关系ts(base_link to map)、tsMap(map to base_link),发现与上述自己计算的一致。
//Rzyx轴旋转
auto tsStamped = buffer.lookupTransform("map", "base_link", ros::Time(0));
//Rzyx轴旋转
auto tsStampedMap = buffer.lookupTransform("base_link", "map", ros::Time(0));
Eigen::Matrix4f ts = tf2::transformToEigen(tsStamped.transform).matrix().cast<float>();
Eigen::Matrix4f tsMap = tf2::transformToEigen(tsStampedMap.transform).matrix().cast<float>();
版权声明:本文为lovelyaiq原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。