开发starter
第一步:创建starter工程hello-spring-boot-starter并配置pom.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>cn.itcast</groupId>
<artifactId>hello-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>第二步:创建配置属性类HelloProperties,用于封装配置文件中配置的参数信息Mybatis从yml读取数据库信息
package cn.itcast.config;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
/*
*读取配置文件转换为bean
* */
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hello")
public class HelloProperties {
private String name;
private String address;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HelloProperties{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}第三步:创建服务类HelloService,作用就是自定义的starter所实现的具体业务
package cn.itcast.service;
public class HelloService {
private String name;
private String address;
public HelloService(String name, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
public String sayHello(){
return "你好!我的名字叫 " + name + ",我来自 " + address;
}
}第四步:创建自动配置类HelloServiceAutoConfiguration,用于自动配置HelloService对象的实例化,@Configuration加上@Bean两个注解实现自动配置,@Configuration和@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)注解很重要,作用在前一篇starter自动配置理解中有讲
package cn.itcast.config;
import cn.itcast.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/*
* 配置类,基于Java代码的bean配置
* */
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
private HelloProperties helloProperties;
//通过构造方法注入配置属性对象HelloProperties
public HelloServiceAutoConfiguration(HelloProperties helloProperties) {
this.helloProperties = helloProperties;
}
//实例化HelloService并载入Spring IoC容器
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public HelloService helloService(){
return new HelloService(helloProperties.getName(),helloProperties.getAddress());
}
}第五步:在resources目录下创建META-INF/spring.factories,作用是描述自动配置类的全路径,让spring boot能够找到自动配置类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
cn.itcast.config.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration至此starter已经开发完成了,可以将当前starter安装到本地maven仓库供其他应用来使用。
使用starter
第一步:创建maven工程myapp并配置pom.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>cn.itcast</groupId>
<artifactId>myapp</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--导入自定义starter-->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.itcast</groupId>
<artifactId>hello-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>第二步:创建application.yml文件,注意编写配置属性类需要的配置属性
server:
port: 8080
hello:
name: xiaoming
address: beijing第三步:创建HelloController
package cn.itcast.controller;
import cn.itcast.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
//HelloService在我们自定义的starter中已经完成了自动配置,所以此处可以直接注入
@Autowired
private HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/say")
public String sayHello(){
return helloService.sayHello();
}
}第四步:创建启动类HelloApplication
package cn.itcast;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class,args);
}
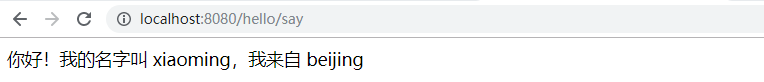
}执行启动类main方法,访问地址http://localhost:8080/hello/say
在前面的案例一中我们通过定义starter,自动配置了一个HelloService实例。本案例我们通过自动配置来创建一个拦截器对象,此对象属于web层的组件,通过此拦截器对象来实现记录日志功能。
我们可以在案例一的基础上继续开发案例二。
开发starter
第一步:在hello-spring-boot-starter的pom.xml文件中追加如下maven坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</dependency>第二步:自定义MyLog注解,作为标识,添加注解的才会被拦截@Target(ElementType.METHOD)注解表示此注解放在方法前@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)注解表示在运行期生效
package cn.itcast.log;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyLog {
/**
* 方法描述
*/
String desc() default "";
}第三步:自定义日志拦截器MyLogInterceptor,拦截器的创建需要继承HandlerInterceptorAdapter,preHandle表示拦截之前执行的方法postHandle表示拦截之后执行的方法
package cn.itcast.log;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* 日志拦截器
*/
public class MyLogInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
private static final ThreadLocal<Long> startTimeThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod)handler;
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();//获得被拦截的方法对象
MyLog myLog = method.getAnnotation(MyLog.class);//获得方法上的注解
if(myLog != null){
//方法上加了MyLog注解,需要进行日志记录
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
startTimeThreadLocal.set(startTime);
}
return true;
}
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod)handler;
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();//获得被拦截的方法对象
MyLog myLog = method.getAnnotation(MyLog.class);//获得方法上的注解
if(myLog != null){
//方法上加了MyLog注解,需要进行日志记录
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Long startTime = startTimeThreadLocal.get();
long optTime = endTime - startTime;
String requestUri = request.getRequestURI();
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." +
method.getName();
String methodDesc = myLog.desc();
System.out.println("请求uri:" + requestUri);
System.out.println("请求方法名:" + methodName);
System.out.println("方法描述:" + methodDesc);
System.out.println("方法执行时间:" + optTime + "ms");
}
}
}第四步:创建自动配置类MyLogAutoConfiguration,用于自动配置拦截器、参数解析器等web组件,因为是web层组件所以需要实现WebMvcConfigurer专门用于web层组件的创建,要注意web层组件的创建同普通的starter创建不同
package cn.itcast.config;
import cn.itcast.log.MyLogInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* 配置类,用于自动配置拦截器、参数解析器等web组件
*/
@Configuration
public class MyLogAutoConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer{
//注册自定义日志拦截器
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new MyLogInterceptor());
}
}第五步:在spring.factories中追加MyLogAutoConfiguration配置
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
cn.itcast.config.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration,\
cn.itcast.config.MyLogAutoConfiguration使用starter
在myapp工程的Controller方法上加入@MyLog注解
package cn.itcast.controller;
import cn.itcast.log.MyLog;
import cn.itcast.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
//HelloService在我们自定义的starter中已经完成了自动配置,所以此处可以直接注入
@Autowired
private HelloService helloService;
@MyLog(desc = "sayHello方法") //日志记录注解
@GetMapping("/say")
public String sayHello(){
return helloService.sayHello();
}
}访问地址:http://localhost:8080/hello/say,查看控制台输出:
请求uri:/hello/say
请求方法名:cn.itcast.controller.HelloController.sayHello
方法描述:sayHello方法
方法执行时间:36ms上述就是自定义的两种starter,结合前篇自动配置starter更加深入理解自动配置的运行原理。
发表回复