Hamilton
该种方法复杂度较高
思路:
dfs + 回溯
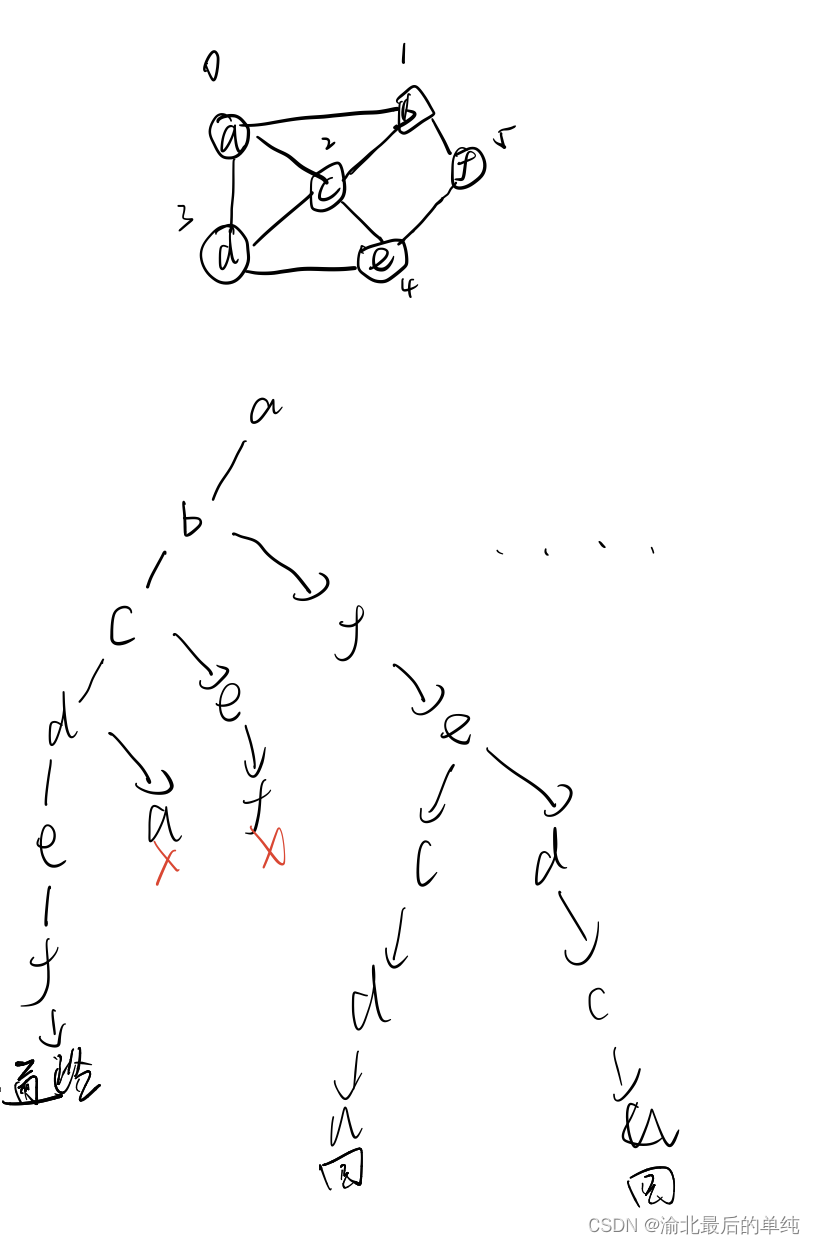
相当于就是以树状的形式 举出 每种可能 。
以下举例部分 情况 以及 代码。
具体思路详见代码。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Hamiton {
public void getHamiltonCircuit(int[][] adjMatrix) {
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[adjMatrix.length]; //用于标记图中顶点是否被访问
int[] path = new int[adjMatrix.length]; //记录哈密顿回路路径
Arrays.fill(isVisited,false);
Arrays.fill(path,-1);
isVisited[0] = true;
path[0] = 0; //从 第一个节点开始 , 选取出发节dian
dfs(adjMatrix, path, isVisited, 1); //dfs查找哈密顿回路
}
public boolean dfs(int[][] adjMatrix, int[] path, boolean[] isVisited, int step) {
if(step == adjMatrix.length) { //当已经遍历完图中所有顶点
if(adjMatrix[path[step - 1]][0] == 1) { // 递归 结束条件 最后一个节点能够回到 第一个节点 输出 路径
System.out.println("哈密顿图");
for (int i = 0; i < path.length; i++)
System.out.print(((char) (path[i] + 'a')) + "——>");
System.out.print(((char) (path[0] + 'a')));
System.out.println();
return false;
}else{ // 哈密顿通路
System.out.println("半哈密顿图");
for (int i = 0; i < path.length - 1; i++)
System.out.print(((char) (path[i] + 'a')) + "——>");
System.out.println((char) (path[path.length - 1] + 'a'));
return false;
}
} else {
for(int i = 0;i < adjMatrix.length;i++) {
if(!isVisited[i] && adjMatrix[path[step - 1]][i] == 1) {
isVisited[i] = true; // 标记访问过该节点
path[step] = i;
if(dfs(adjMatrix, path, isVisited, step + 1))
return true;
else {
isVisited[i] = false; //回溯
path[step] = -1;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hamiton test = new Hamiton();
// 示例矩阵
int[][] adjMatrix = {
{-1,1,1,1,-1,-1},
{1,-1,1,-1,-1,1},
{1,1,-1,1,1,-1},
{1,-1,1,-1,1,-1},
{-1,-1,1,1,-1,1},
{-1,1,-1,-1,1,-1}
};
test.getHamiltonCircuit(adjMatrix);
task(test);
}
// 12.24 作业演示
public static void task(Hamiton test){
int[][] a ={
{-1,1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1},
{-1,-1,1,-1,1,-1,-1},
{-1,1,-1,1,1,-1,-1},
{-1,-1,1,-1,1,-1,-1},
{-1,1,1,1,-1,1,-1},
{-1,-1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1},
{-1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,-1},
};
System.out.println("ans : ");
test.getHamiltonCircuit(a);
int[][] b = new int[11][11];
int[][] routes = {
{0,1},
{0,3},
{0,4},
{0,6},
{1,2},
{1,7},
{2,5},
{2,3},
{3,8},
{3,10},
{4,5},
{4,9},
{5,6},
{5,7},
{5,8},
{6,10},
{7,10},
{8,9},
{9,10}
};
init(b,routes);
System.out.println("ans : ");
test.getHamiltonCircuit(b);
}
public static void init(int[][] martrix,int[][] routes) {
for(int[] arr : routes){
martrix[arr[0]][arr[1]] = 1;
martrix[arr[1]][arr[0]] = 1;
}
}
}
半哈密顿图
a——>b——>c——>d——>e——>f
哈密顿图
a——>b——>f——>e——>c——>d——>a
哈密顿图
a——>b——>f——>e——>d——>c——>a
哈密顿图
a——>c——>b——>f——>e——>d——>a
哈密顿图
a——>c——>d——>e——>f——>b——>a
半哈密顿图
a——>d——>c——>b——>f——>e
哈密顿图
a——>d——>c——>e——>f——>b——>a
半哈密顿图
a——>d——>e——>c——>b——>f
哈密顿图
a——>d——>e——>f——>b——>c——>a
我是菜鸡,这应该是最简单的查找方法 复杂度 极高 ,更高深的详见百度。
12.23日作业 运行示例 结果
(a):
(b):

版权声明:本文为qq_57115378原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。