Spring Boot日志
1.SLF4j使用
(1)如何在系统中使用SLF4j
开发中,日志记录方法的调用,不应该来直接调用日志的实现类,而是调用日志抽象层里面的方法。给系统里面导入slf4j的jar和logback的实现jar
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String[] args){
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);
logger.info("Hello World");
}
}
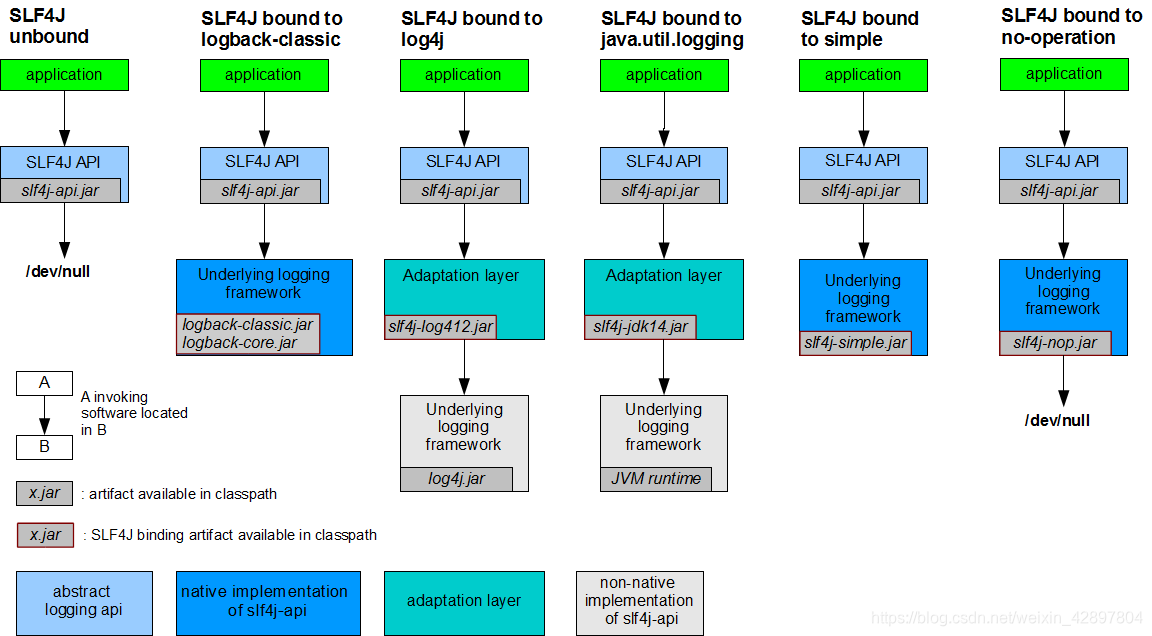
每一个日志的实现框架都有自己的配置文件。使用slf4j以后,配置文件还是做成日志实现框架的配置文件
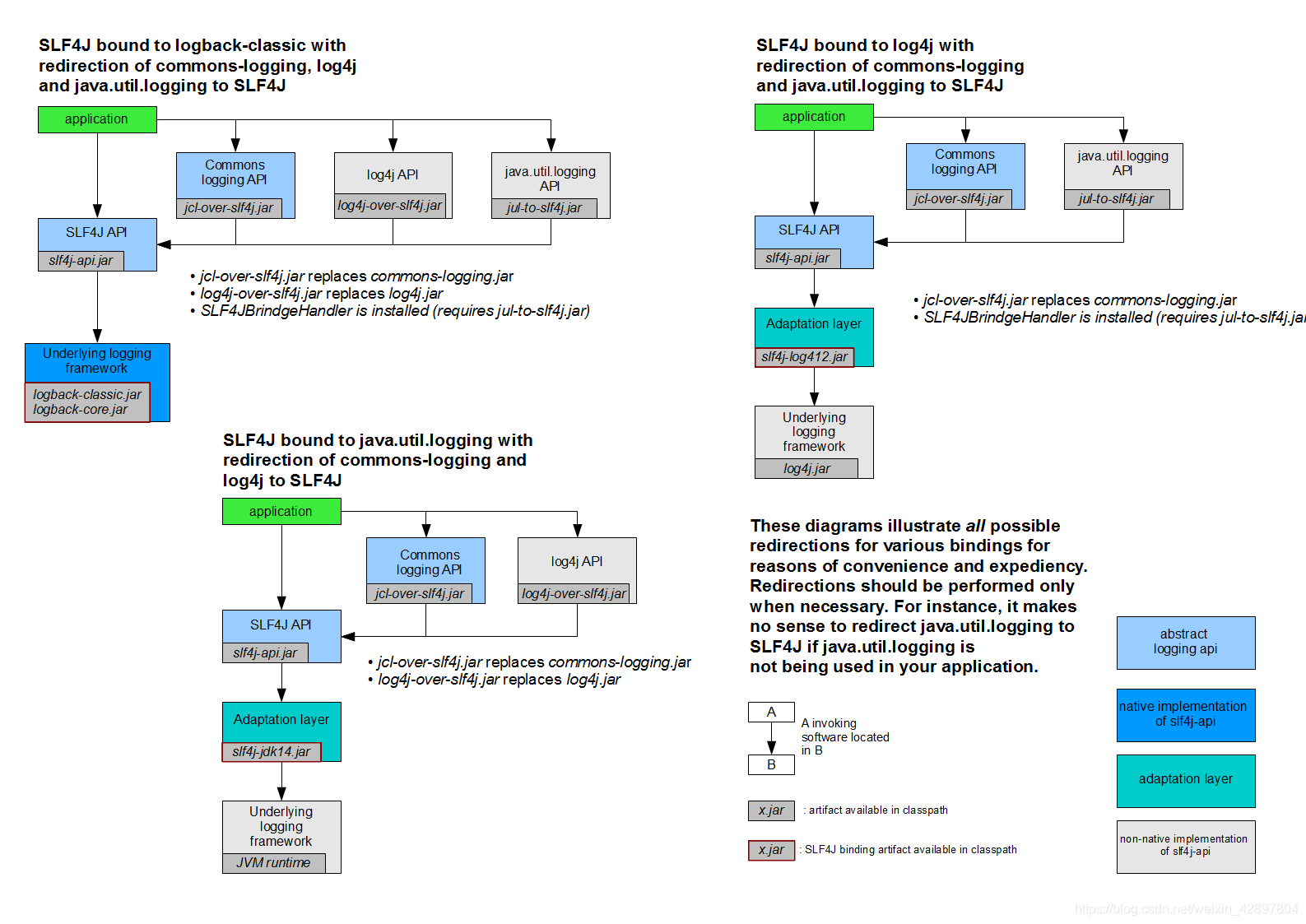
(2)如何让系统中所有的日志都统一到slf4j
(1)将系统中其他日志框架先排除出去
(2)用中间包来替换原有的日志框架
(3)我们导入slf4j其他的实现
2.日志关系

总结:
(1)SpringBoot底层也是使用slf4j+logback的方式进行日志记录
(2)SpringBoot也把其他的日志都替换成了slf4j
注意:如果我们要引入其他框架,一定要把这个框架的默认日志依赖移除掉。
SpringBoot能自动适配所有的日志,而且底层使用slf4j+logback的方式记录日志,引入其他框架的时候,只需要把这个框架依赖的日志框架派出的
3.日志使用
/**
* 记录器
*/
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//日志的级别
//由低到高 trace<debug<info<warn<error
//可以调整输出的日志级别,日志就只会在这个级别以后的高级别生效
logger.trace("这是trace日志...");
logger.debug("这是debug日志...");
//SpringBoot默认给我们使用的是info级别的
logger.info("这是debug日志...");
logger.warn("这是warn日志...");
logger.error("这是error日志...");
}
(1)指定配置
给类路径下放上每个日志框架自己的配置文件即可,SpringBoot就不使用默认配置
logback.xml:直接就被日志框架识别
logback-spring.xml:日志框架不直接加载日志的配置项,而由SpringBoot解析日志配置,可以使用SpringBoot的高级功能Profile功能
<springProfile name="staging">
可以指定某段配置只在某个环境下生效
</springProfile>
Spring Boot Web开发简介
1.使用Spring Boot
(1)创建SpringBoot应用,选择需要的模板
(2)SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行
(3)编写业务代码
2.自动配置原理
3.对静态资源的映射规则
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.resources",
ignoreUnknownFields = false
)
public class ResourceProperties {
//可以设置和资源有关的参数,比如:缓存时间等
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
} else {
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{"/webjars/**"}).addResourceLocations(new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"}).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{staticPathPattern}).addResourceLocations(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations())).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
}
(1)所有/webjars/**,都去classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/找资源。webjars:以jar包的方式引入静态资源
webjars官方网站
http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js
<!-- 引入jquery-webjar -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1</version>
</dependency>
(2)”/**”访问当前项目的任何资源(静态资源的文件夹)
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/",
"classpath:/public/"
"/" //当前项目的根路径
(3)欢迎页,静态资源文件夹下的所有indx.html页面,被”/**”映射
//配置欢迎页的映射
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext, FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, this.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(this.getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}
(4)所有的 **/favicon.ico 都是在静态资源文件下找
Thymeleaf入门
1.模板引擎
JSP、Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf
2.模板引擎思想(作用)
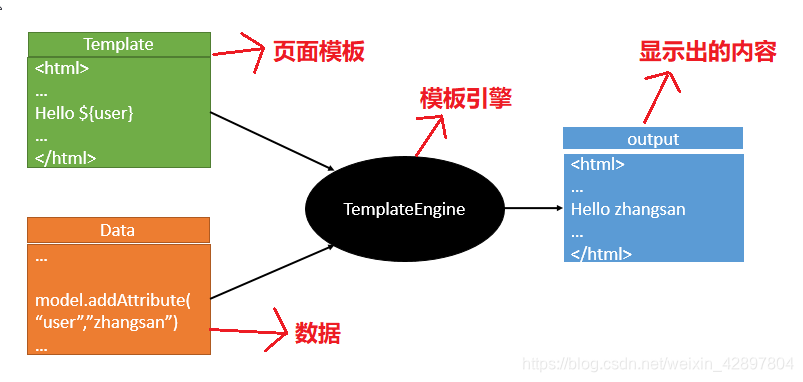
SpringBoot推荐的Thymeleaf,语法更简单,功能更强大。
3.引入模板引擎
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
4.Thymeleaf使用&语法
(1)Thymeleaf使用
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.thymeleaf"
)
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true;
private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/";
private String suffix = ".html";
只要把HTML页面放在classpath:/templates/,thymeleaf就能自动渲染;
(2)Thymeleaf语法
(1)导入thymeleaf的名称空间
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
(2)语法规则
th:text 改变当前元素里面的文本内容
th 可搭配任意HTML属性,例如:th:href,来替换原生属性的值。
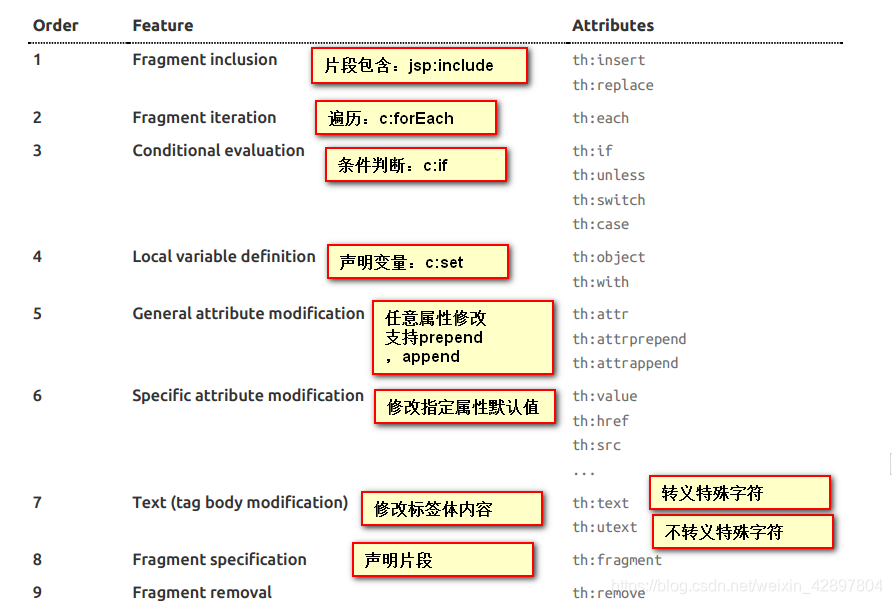
(3)表达式
Simple expressions:(表达式语法)
Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL;
1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法
2)、使用内置的基本对象:
${session.foo}
3)、内置的一些工具对象;
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;
补充:配合 th:object="${session.user}";
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...};
选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;
补充:配合 th:object="${session.user}";
<div th:object="${session.user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p>
<p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p>
<p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p>
</div>
Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容
Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL;
@{/order/process(execId=${execId},execType='FAST')}
Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式
<div th:insert="~{commons :: main}">...</div>
Literals(字面量)
Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…
Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…
Boolean literals: true , false
Null literal: null
Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,…
Text operations:(文本操作)
String concatenation: +
Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|
Arithmetic operations:(数学运算)
Binary operators: + , ‐ , * , / , %
Boolean operations:(布尔运算)
Binary operators: and , or
Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not
Comparisons and equality:(比较运算)
Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )
Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符)
If‐then: (if) ? (then)
If‐then‐else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
Special tokens:
No‐Operation: _
数据访问
1.JDBC
(1)引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
(2)在主配置文件中进行配置
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql:///huawen
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
(3)自动配置原理
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc
(1)参考DataSourceConfiguration
根据配置创建数据源,默认使用Hikari连接池,可以使用 spring.datasource.type指定自定义的数据源类型。
(2)SpringBoot默认可以支持
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource、HikariDataSource、BasicDataSource
(3)自定义数据源类型
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({DataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"spring.datasource.type"}
)
static class Generic {
Generic() {
}
@Bean
DataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
//使用DataSourceBuilder创建数据源,利用反射创建响应type的数据源,并且绑定相关属性
return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
}
}
2.整合Druid数据源
(1)引入Druid依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
(2)配置主配置文件
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql:///huawen
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#数据源其他配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,'wall'用于防火墙
filters: stat,wall,slf4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
/**
* 测试类
*/
@SpringBootTest
class SpringBoot05ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
}
}
数据源其他配置需要在配置类中配置,才能起作用

(3)整合Druid详细配置类
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource druid(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//配置Druid的监控
/**
* 1、配置一个管理后台的Servlet
* @return
*/
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
Map<String,String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
//设置Druid后台管理登录名和登录密码
initParams.put("loginUsername","admin");
initParams.put("loginPassword","123456");
/*设置允许访问的路径,默认允许所有可访问*/
initParams.put("allow","");
/*设置拒绝访问的路径
initParams.put("deny","");*/
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
return bean;
}
/**
* 2、配置Web监控的filter
* @return
*/
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
Map<String,String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*");
bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));
return bean;
}
}
3.整合MyBatis
(1)引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2</version>
</dependency>
(2)注解实现
//指定这是一个操作数据库的mapper
@Mapper
public interface NewsMapper {
/**
* 按ID查询数据
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from t_news where id = #{id}")
News getNewsById(String id);
}
//使用MapperScan批量扫描所有的Mapper接口;
@MapperScan(value = "com.guan.springboot06.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBoot06Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBoot06Application.class, args);
}
}
如果数据库字段命名为下划线命名法(xx_xx),而实体类字段命名为驼峰命名法(xxXx),该如何映射?
自定义MyBatis的配置规则,给容器中添加一个ConfigurationCustomizer。
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public ConfigurationCustomizer configurationCustomizer() {
return new ConfigurationCustomizer(){
@Override
public void customize(Configuration configuration) {
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true);
}
};
}
}
(3)配置文件实现
(1)创建mybatis主配置文件和映射文件
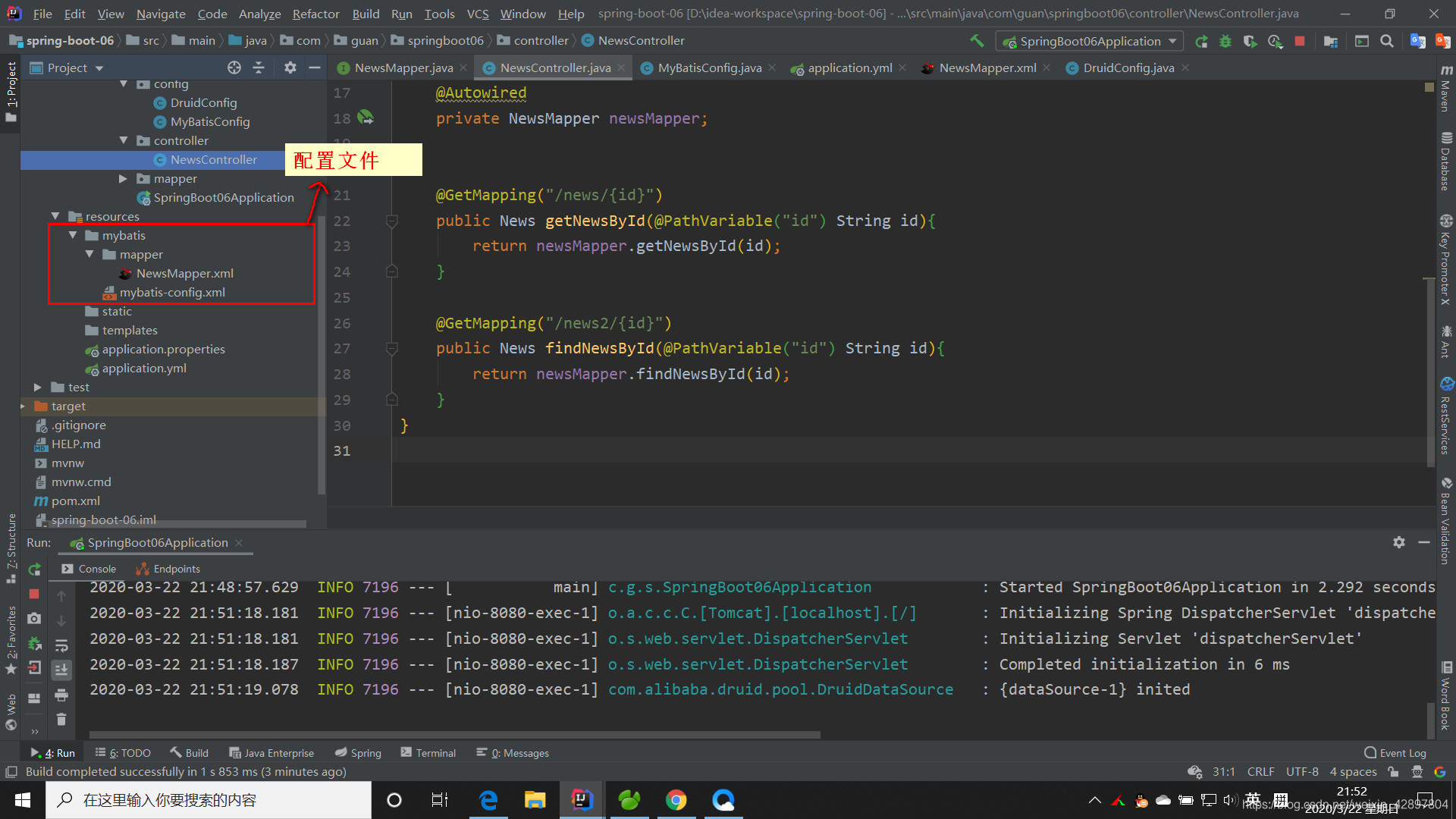
(2)配置主配置文件
mybatis:
#指定全局配置文件的位置
config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
#指定sql映射文件的位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
4. Spring Data JPA
(1)引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
(2)配置主配置文件
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql:///jpa?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jpa:
hibernate:
#更新或者创建数据表结构
ddl-auto: update
#控制台显示SQL
show-sql: true
(3)创建实体类
/**
* @author
* 使用JPA注解配置映射关系
*/
@Entity //告诉JPA这是一个实体类(和数据库表映射的类)
@Table(name = "t_user") //指定和哪个数据库表对应;如果省略默认表明就是实体类名
public class User {
@Id //这是一个主键
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) //自增主键
/**
* 主键ID
*/
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "name", length = 50) //和数据库表对应的列
private String name;
@Column //省略默认列名就是属性名
private String email;
如果@Table(name = “t_user”)注解报错Cannot resolve table ‘xx’,可以使用以下方法解决。
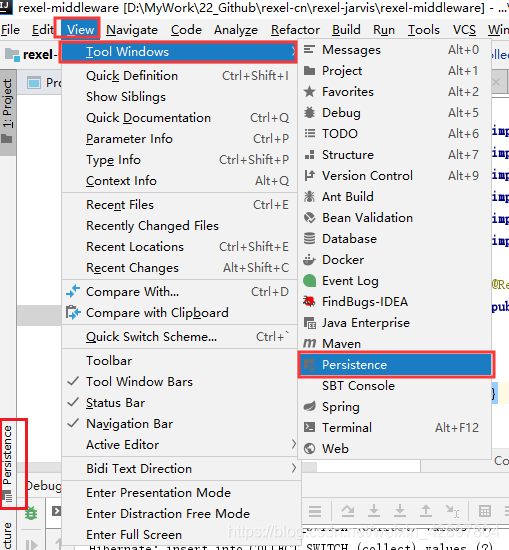
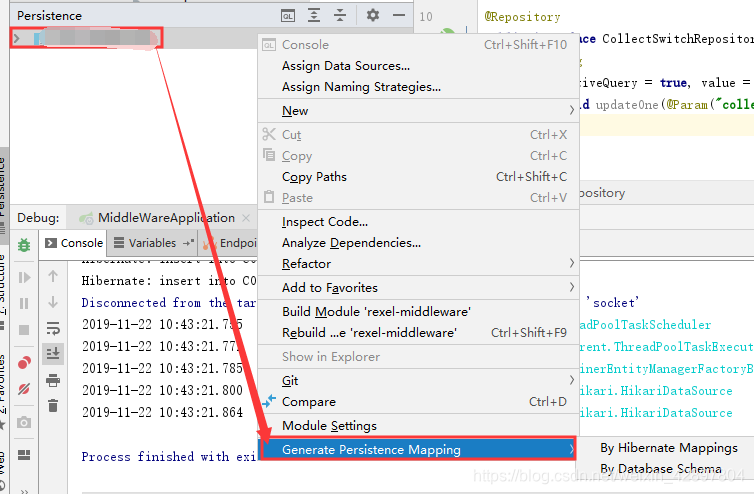
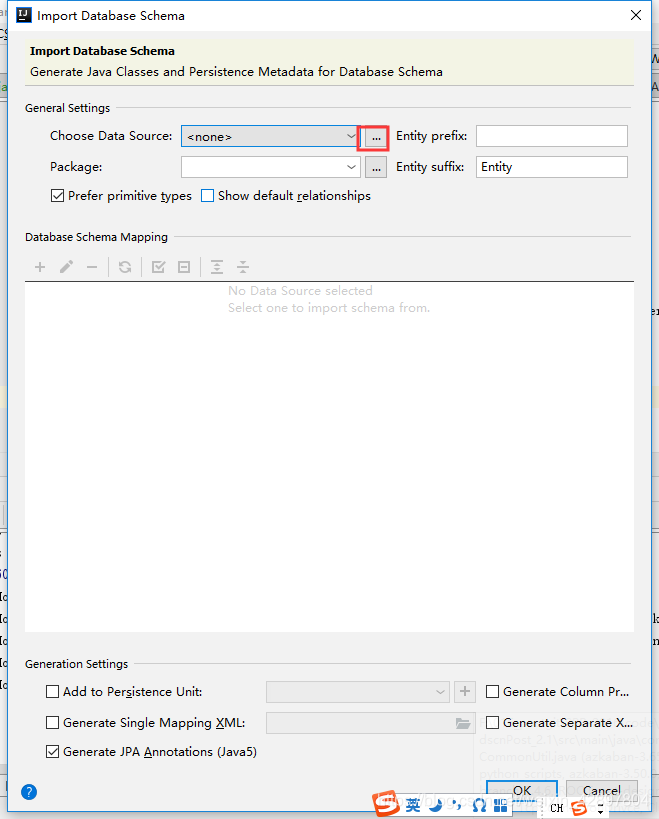
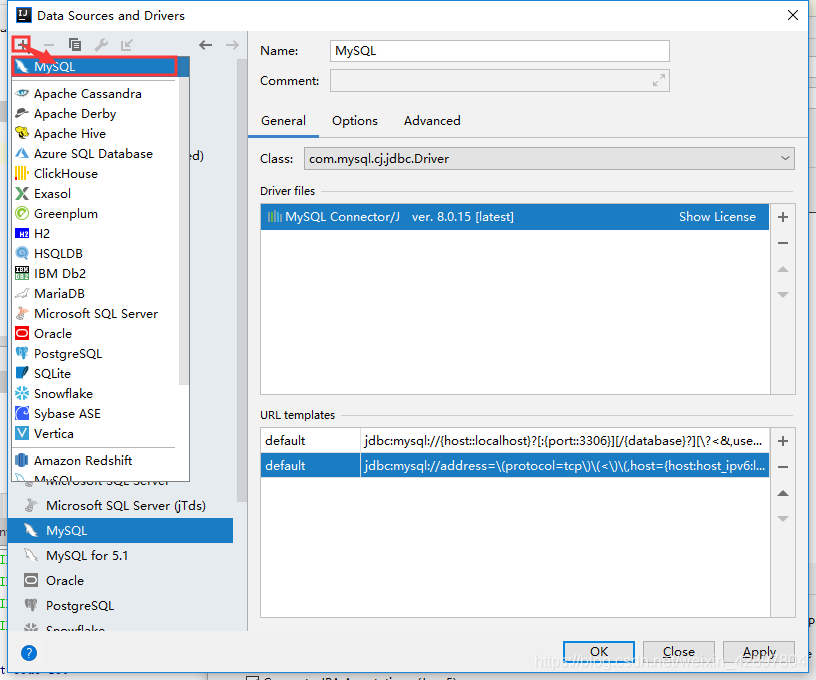
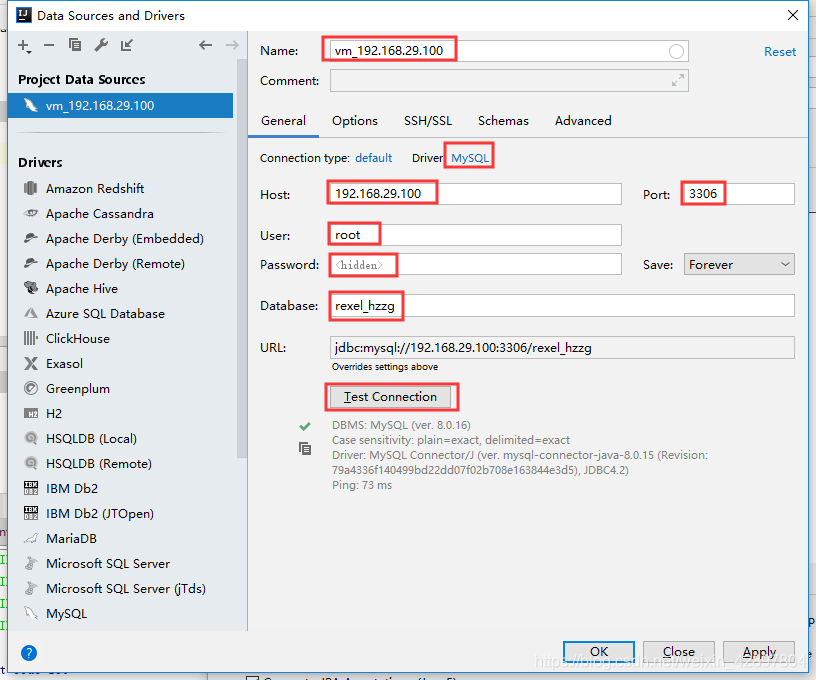
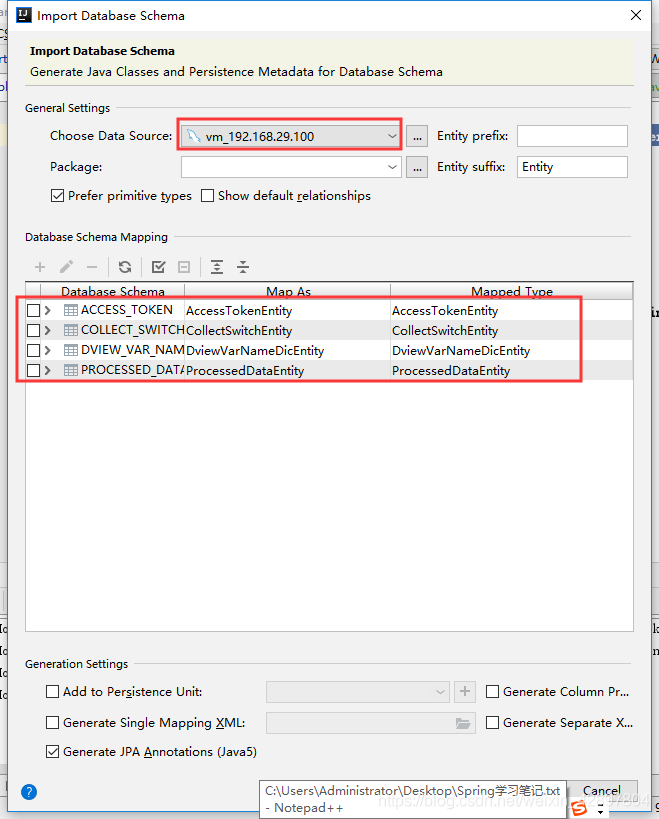
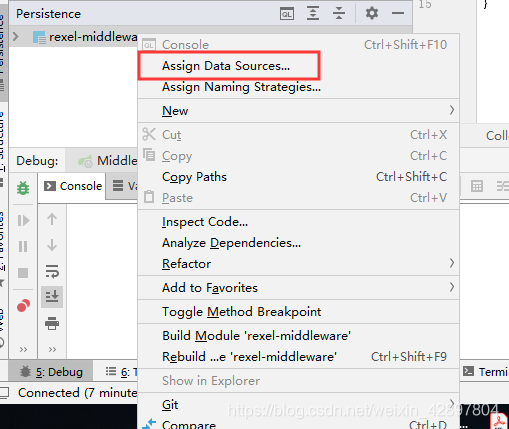
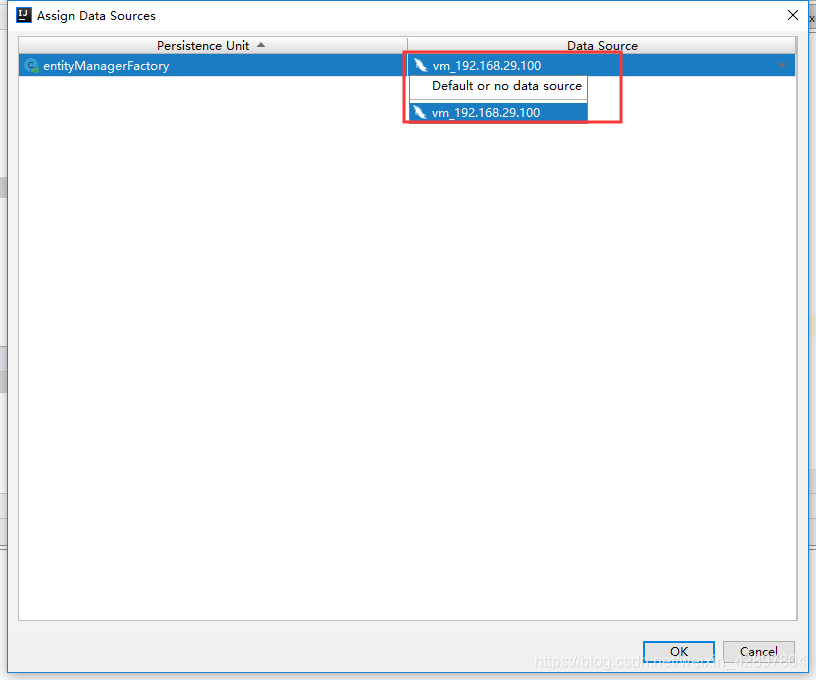
(4)编写Dao接口来操作实体类对应的数据表(Repository)
/**
* @author 11653
* 继承JpaRepository来完成对数据库的操作
*/
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> {
}
(5)编写Controller类中的方法
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public User findUserById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
User user = userRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
return user;
}
@GetMapping("/user")
public User insertUser(User user){
User user1 = userRepository.save(user);
return user1;
}
}