time():
C 库函数 time_t time(time_t *seconds) 返回自纪元 Epoch(1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC)起经过的时间,以秒为单位。如果 seconds 不为空,则返回值也存储在变量 seconds 中。
ctime():
C 库函数 char *ctime(const time_t *timer) 返回一个表示当地时间的字符串,当地时间是基于参数 timer。
返回的字符串格式如下: Www Mmm dd hh:mm:ss yyyy 其中,Www 表示星期几,Mmm 是以字母表示的月份,dd 表示一月中的第几天,hh:mm:ss 表示时间,yyyy 表示年份。
声明:
time_t time(time_t *seconds)参数:seconds — 这是指向类型为 time_t 的对象的指针,用来存储 seconds 的值。
返回值:以 time_t 对象返回当前日历时间。
定时器代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
time_t current, start;
int m = ???? //定时的时间,单位为s
int main()
{
time(&start);
cout << ctime(&start) << '\n';
do
{
//操作数
time(¤t);
}
while((current - start) != m);
cout << ctime(¤t) << '\n';
return 0;
}
下面给出一个全排列计时的栗子, 全排列实现方法为dfs,也可以理解为怎么在dfs中进行计时终结
全排列说明:
当 n = 4 时,共有 n!= 24 个全排列顺序,分别为:
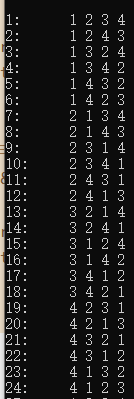
可是我们知道,当 n = 10 时, n! = 3628800,但我们在跑数据的时候,只想跑5s或者10s的数据,这时候如何终止呢?
这里直接给出定时输出截图和代码,不懂的或者有更好方法的可在底下评论噢~~~~
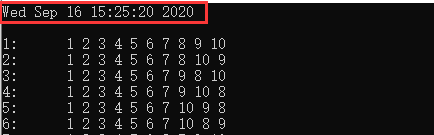
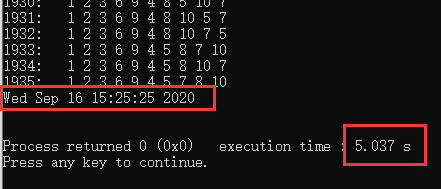
由截图我们知道,大致运行时间是5s,虽然不是很精准,但应付一些定时需要还是有用的~~~~
运行代码:
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
const int MAXN = 5*100005;
const double r = 0.57721566490153286060651209;//欧拉常数
const double pi = acos(-1);
static vector<int>x;
int ans = 1, flag = 1;
time_t current, start;
int m = 5, n = 10; //定时5s,全排序n=10
void GG(int c, int n)
{
if((current - start) >= m)
{
if(flag) //输出一次时间
cout << ctime(¤t) << '\n';
flag = 0;
return ;
}
if(c <= n)
for(int i=c; i<=n; ++i)
{
swap(x[c], x[i]);
GG(c+1, n);
swap(x[c], x[i]);
time(¤t);
}
else
{
cout << ans << ": \t";
for(auto i: x)
if(i != 0)
cout << i << ' ';
ans++;
cout << '\n';
return ;
}
}
int main()
{
for(int i=0; i<=n; ++i)
x.push_back(i);
time(&start);
cout << ctime(&start) << '\n';
do
{
GG(1, n);
time(¤t);
}
while((current - start) != m);
//cout << ctime(¤t) << '\n';
return 0;
}
版权声明:本文为weixin_43237242原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。