Redis简介
Redis是一个高性能的内存数据库,以key-value方式存储数据,可以作为缓存使用。
为什么使用缓存?
-
高并发
MySQL的连接数存在瓶颈,连接过大可能导致MySQL宕机
解决方法:
- 部署多个MySQL服务,主从复制
- 部署缓存,承担一部分的并发
-
高性能
基于内存,内存IO效率远远高于磁盘
Redis的特点:
- 性能高(读的速度是110000次/s,写的速度是81000次/s,单机redis支撑万级并发)
- 支持多种存储类型
- 丰富的特性(发布订阅、事务、过期策略等)
- 支持持久化
- 单线程 (避免上下文切换,线程同步问题)
Redis安装和使用
Linux安装
- 先安装gcc编译器,可以用来编译c、c++等代码
yum -y install gcc //-y表示自动安装
- 安装Redis
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-3.2.5.tar.gz //下载redis安装包到usr/local
tar xzf redis-2.8.17.tar.gz
cd redis-2.8.17
make
- BUG
使用 make MALLOC=libc 进行编译。MALLOC表示C语言中的动态分配内存函数,libc就是库文件
Windows安装
- 从官网下载redis的windows版本
- 解压
- 启动服务器端
- 启动客户端
Redis的配置
redis.conf
- 注释掉 bind 127.0.0.1
- 关闭保护模式 protected mode no
使用Redis
- 1、启动服务器 src中 ./redis-server …/redis.conf
- 2、启动客户端 src中 ./redis-cli
Redis的数据类型
Redis的数据以key-value方式存储。
数据类型有:
- string 字符串(简单的key-value数据,适合保存单个数据,如:用户数量、库存数、商品数)
- hash 哈希(适合保存复杂类型数据,如:用户对象)
- list 列表(链表结构,适合保存有序的、可重复的数据,如:商品列表、评论列表)
- set 无序集合(适合保存无序的,不可重复的数据)
- zset 有序集合(适合保存有序的,不可重复的数据)
字符串
set key value
get key
可以设置失效时间
set key value EX 10 //10秒钟之后失效
Hash
hash存储,一般可以用来存储Java中的一个完整的自定义对象。
//hmset是存储hash值的指令,
//user是当前hash的key
//name "zhangsan" age 23 sex "nan" 是 key对应的值
127.0.0.1:6379> hmset user name "zhangsan" age 23 sex "nan"
OK
//hmget获取hash中的某一个属性的值
127.0.0.1:6379> hmget user name
1) "zhangsan"
127.0.0.1:6379> hmget user age
1) "23"
//hgetall是获取hash中的所有属性对应的值
127.0.0.1:6379> hgetall user
1) "name"
2) "zhangsan"
3) "age"
4) "23"
5) "sex"
6) "nan"
List列表(有序列表)
采用的链表结构进行数据存储
lpush 从右向左添加
rpush 从左向右添加
lrange key start stop
//lpush用来存储一个列表的命令。interesting是列表的名称,"basketball"列表中的值
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush interesting "basketball"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush interesting "football" "ball"
(integer) 3
//lrange输出列表中的数据的命令, interesting就是列表的名称 。 0 2是列表的开始输出索引和结束索引。
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange interesting 0 2
1) "ball"
2) "football"
3) "basketball"
Set集合(无序集合)
不能有重复的数据。
sadd key member //存数据
smembers key //取数据
案例:
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd strset "a" "b" "c"
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> smembers strset
1) "b"
2) "c"
3) "a"
zset集合(有序集合)
zadd key score member (score是一个数字,zset就是通过这个数字进行排序,可以重复)
zrangebyscore key 0 1000 //通过分数排序输出
有序集合是按照score进行排序
SpringBoot整合Redis
1)依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2)配置文件
spring.redis.host=localhost
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.database=0
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=100
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=100ms
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=100
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=10
3)配置RedisTemplate
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<String, Object>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
// key采用String的序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
// hash的key也采用String的序列化方式
template.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
// value序列化方式采用jackson
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
// hash的value序列化方式采用jackson
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}
4)使用RestTemplate
常用方法:
- opsForValue 获得string类型的操作对象
- opsForHash 获得hash类型的操作对象
…
5) 缓存使用的流程
按id查询商品的过程
1) 以id为键查询Redis缓存,如果能查到就返回数据,结束
2)如果查不到,就查询数据库,数据库查到,缓存到Redis,返回数据
3)如果数据库查不到,返回null,结束
4)增删改数据库的同时,要修改缓存
@Service
public class GoodsServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<GoodsMapper, Goods> implements IGoodsService {
public static final String TYPE = "GOODS-";
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate;
public Goods getGoodsById(Long id){
ValueOperations<String, Object> ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
//1) 以id为键查询Redis缓存,如果能查到就返回数据,结束
Object value = ops.get(TYPE + id);
//2)如果查不到,就查询数据库
if(value == null){
System.out.println("缓存不存在,查询数据库");
// 数据库查到,缓存到Redis,返回
Goods goods = this.getById(id);
if(goods != null){
System.out.println("数据库存在,保存到缓存");
ops.set(TYPE + id,goods);
}else{
System.out.println("数据库不存在,返回null");
}
return goods;
}else{
System.out.println("缓存存在,返回"+value);
//如果能查到就返回数据,结束
return (Goods) value;
}
}
}
Redis的常见问题
1)缓存击穿
高并发的情况下,短时间内缓存会被穿过,请求直接打到数据库上,可能导致数据库压力过大。
解决方案:对代码上锁(双重检查锁)
2)缓存穿透
高并发的情况下,如果查询不存在的数据,因为缓存和数据库都不存在,请求都会打到数据库上,可能导致系统崩溃。
解决方案:
1) 保存不存在的数据到缓存中,设置一定过期时间
2) 布隆过滤器(直接过滤掉不存在数据的请求) 不能准确判断是否存在数据,能准确判断数据不存在
3)缓存雪崩
高并发的情况下,缓存服务器重启或热点数据同时过期,全部访问数据库,导致数据库宕机
解决方案:
1)配置缓存集群
2)尽量给热点数据设置不一样的过期时间,相对均匀
解决代码
public Goods getGoodsById(Long id){
ValueOperations<String, Object> ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Object value = ops.get(TYPE + id);
//外层先读缓存,缓存如果有,就不执行同步块
if(value == null) {
synchronized (this) {
//1) 以id为键查询Redis缓存,如果能查到就返回数据,结束
value = ops.get(TYPE + id);
//2)如果查不到,就查询数据库
if (value == null) {
System.out.println("缓存不存在,查询数据库");
// 数据库查到,缓存到Redis,返回
Goods goods = this.getById(id);
if (goods != null) {
System.out.println("数据库存在,保存到缓存");
ops.set(TYPE + id, goods);
} else {
System.out.println("数据库不存在,返回null");
//保存空数据到缓存中,设置过期时间
ops.set(TYPE + id,new Goods(),30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
return goods;
} else {
System.out.println("缓存存在,返回" + value);
//如果能查到就返回数据,结束
return (Goods) value;
}
}
}
System.out.println("缓存存在,返回" + value);
return (Goods) value;
}
JMeter配置
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Q5FDXmxy-1654994394888)(imgs/1621326466856.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d865a5630e644b7fbce16ebf3bfb346a.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-VGrZu3IH-1654994394890)(imgs/1621326457465.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e9ba1c2e15e64a6dbf5c99d91f0866d7.png)
声明式缓存
SpringBoot项目需要的依赖,配置文件同上
1.在启动类上添加注解 @EnableCaching
2.Redis的配置类
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisCacheConfiguration provideRedisCacheConfiguration(){
//加载默认配置
RedisCacheConfiguration conf = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
//返回Jackson序列化器
return conf.serializeValuesWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
}
}
3)缓存注解
-
@CacheConfig 使用在Service类上,如:@CacheConfig(cacheNames = “books”)
-
@Cacheable 使用在查询方法上,让方法优先查询缓存
-
@CachePut 使用在更新和添加方法上,数据库更新和插入数据后同时保存到缓存里
-
@CacheEvict 使用在删除方法上,数据库删除后同时删除缓存
注意:实体类必须实现序列化接口
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "brand")
@Service
public class BrandServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<BrandMapper, Brand> implements IBrandService {
@Autowired
private BrandMapper brandMapper;
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "brand-category",key = "T(String).valueOf(#cid)")
@Override
public List<Brand> findBrandsByCategory(Integer cid) {
return brandMapper.selectBrandsByCategory(cid);
}
@Cacheable(key = "T(String).valueOf(#id)")
@Override
public Brand findBrandById(Long id) {
return this.getById(id);
}
@CachePut(key = "T(String).valueOf(#brand.id)")
@Override
public Brand saveBrand(Brand brand) {
this.saveOrUpdate(brand);
return brand;
}
@CacheEvict(key = "T(String).valueOf(#id)")
@Override
public void deleteBrand(Long id) {
this.removeById(id);
}
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "brand-page",key = "T(String).valueOf(#page)")
@Override
public IPage<Brand> pageBrands(Long page) {
return this.page(new Page<>(page,10));
}
}
事务
Redis的事务是将一系列操作打包,一起提交。没有原子性,隔离性的,也没有回滚事务。
multi 启动事务
exec 提交事务
discard 放弃事务
watch 监视某个数据,如果修改该数据时,在另一个事务中对该数据进行了修改,当前的修改就被放弃
总结:
事务中如果出现语法错误,整个事务无法执行;如果出现数据错误,事务可以成功一部分,失败一部分。
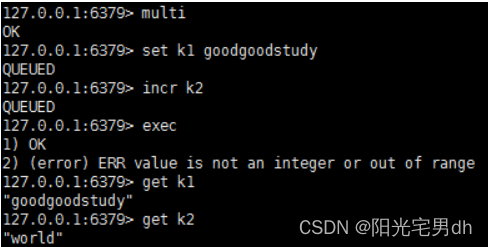
PS:incr 增加数值,decr 减少数值
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-AnAFOA0E-1654994394891)(Redis.assets/image-20211222163247371.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f49581de5b8948dda980f2691a4fb741.png)
出现语法错误,整个事务失败
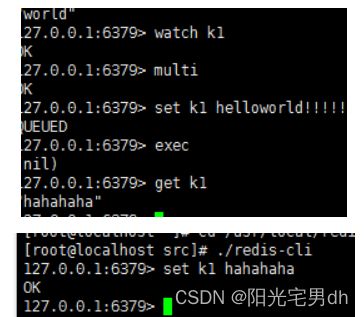
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-cHardUVo-1654994394893)(Redis.assets/image-20211222163645871.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5226256ebb67460cb63c6a91f6508341.png)
出现运算错误,事务一部分成功,一部分失败
监视某个键,当前客户端事务提交前,键被其它事务修改,当前事务就放弃键的修改
持久化策略
为什么持久化?Redis属于内存式数据库,程序关闭后数据会清空,有时候需要将内存中的数据长期在文件保存起来
持久化策略
-
AOF:默认每秒对数据进行持久化
-
RDB:按条件触发持久化操作(任意一个)
900 1 900秒中修改1次
300 10 300秒中修改10次
60 10000 60秒中修改10000次
配置方法
RDB
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-6MVSpYIy-1654994394895)(imgs/clipboard.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/95e950ec1e0e49ffa4955a210b41508f.png)
AOF
appendonly yes / no yes开启AOF
appendfsync everysec 每秒保存
如何选择?
允许少量数据丢失,性能比较高—-RDB
只允许很少数据丢失—-AOF
不允许数据丢失—-RDB + AOF
淘汰策略
为什么要淘汰?Redis数据保存在内存中,数据太多会出现溢出问题,Redis会根据某些策略淘汰一些数据
64位系统,上限就是内存上限;32位最大4G
配置最大内存:
max-memory 配置0就是无上限(默认)
LRU算法:Least Recently Used 最近最少使用算法,淘汰长期不用的缓存
淘汰策略:
maxmemory-policy
值:
noevication(默认) 不淘汰
allkeys-lru(推荐) 使用LRU淘汰比较少使用的键
volatile-lru 在过期的键中淘汰较少使用的
allkeys-random 在所有键中随机淘汰
volatile-random 在过期键中随机淘汰
volatile-ttl 在过期键中淘汰存活时间短的键