这篇文章是我前面一篇文章的后续(https://blog.csdn.net/xiaobai1_1/article/details/103261272)
前面一篇文章已经把从维基百科下载的xml格式的数据转换成了json格式的文件。这里我们就用转换好的json文件开始下面的工作:
1、mysql数据库连接
import pymysql
def prem(db):
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute("SELECT VERSION()")
data = cursor.fetchone()
print("Database version : %s " % data) # 结果表明已经连接成功
if __name__ == "__main__": # 起到一个初始化或者调用函数的作用
db = pymysql.connect("127.0.0.1", "admin", "root", "zhwiki", charset='utf8mb4')
cursor = db.cursor()
prem(db)
reviewdata_insert(db)
cursor.close()
2、创建表
我们先来看一下json里面有些什么东西:
写了一个test来看一下,这里我们用 i 来控制输出的条数,这里我们只输出了一条进行查看:
from smart_open import smart_open
import json
x = 0
for line in smart_open('zhwiki-latest.json.gz'):
article = json.loads(line)
print("Article title: %s" % article['title'])
for section_title, section_text in zip(article['section_titles'], article['section_texts']):
print("Section title: %s" % section_title)
print("Section text: %s" % section_text)
x += 1
if x == 1:
break
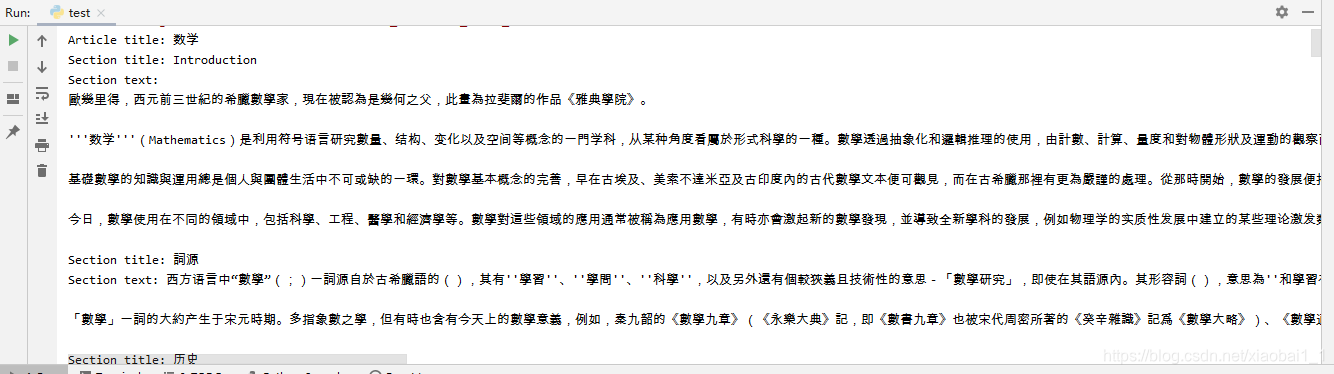
看到我们输出的内容后,可以根据其需求建表
sql = """CREATE TABLE review (
Article_title VARCHAR(1000),
section_title VARCHAR(1000),
section_text mediumtext
)"""
cursor.execute(sql) # 根据需要创建一个表格
3、简析json文件
用json.loads()进行简析
for line in smart_open('zhwiki-latest.json.gz'):
review_text = json.loads(line)
将json文件导入mysql数据库完整程序(经历的时间较长):
import json
from smart_open import smart_open
import pymysql
def prem(db):
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute("SELECT VERSION()")
data = cursor.fetchone()
print("Database version : %s " % data) # 结果表明已经连接成功
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS review") # 习惯性
sql = """CREATE TABLE review (
Article_title VARCHAR(1000),
section_title VARCHAR(1000),
section_text mediumtext
)"""
cursor.execute(sql) # 根据需要创建一个表格
def reviewdata_insert(db):
try:
# lines = f.readline() # 使用逐行读取的方法
# review_text = json.loads(lines) # 解析每一行数据
for line in smart_open('zhwiki-latest.json.gz'):
review_text = json.loads(line)
article_title= review_text['title']
print("Article title: %s" % article_title)
for section_titles, section_texts in zip(review_text['section_titles'],review_text['section_texts']):
# section_titles=review_text['section_titles']
#section_texts=review_text['section_texts']
print("Section title: %s" % section_titles)
print("Section text: %s" % section_texts)
inesrt_re = "insert into review(Article_title,section_title, section_text) values(%s,%s,%s)"
data= ( article_title, section_titles, section_texts)
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute(inesrt_re,data)
db.commit()
except Exception as e:
db.rollback()
print(str(e))
break
if __name__ == "__main__": # 起到一个初始化或者调用函数的作用
db = pymysql.connect("127.0.0.1", "admin", "root", "zhwiki", charset='utf8mb4')
cursor = db.cursor()
prem(db)
reviewdata_insert(db)
cursor.close()
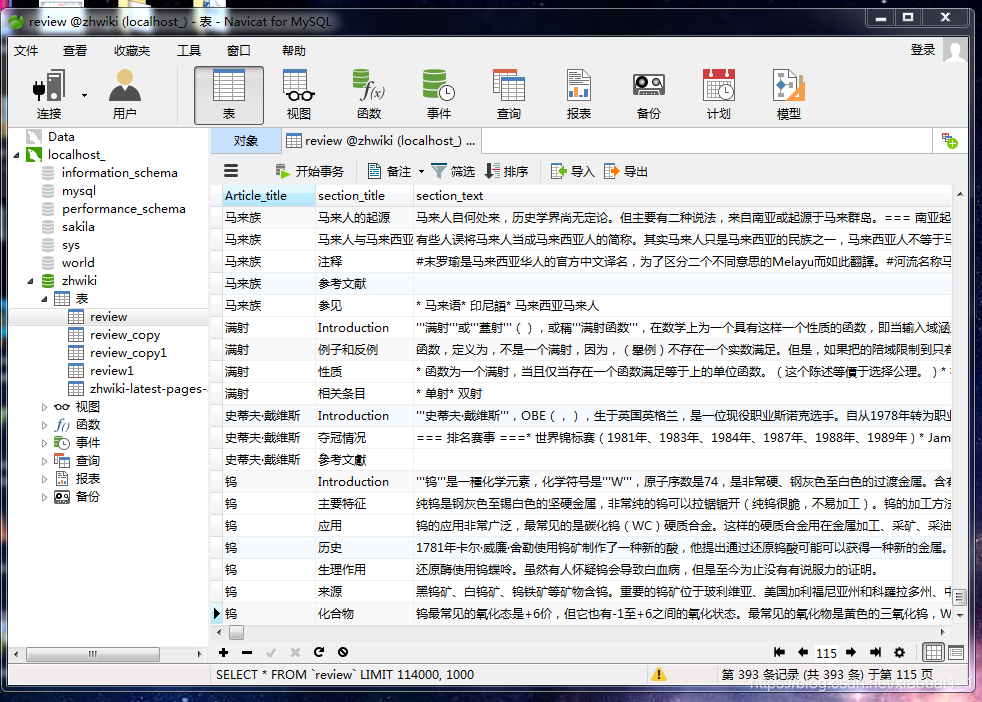
4、对数据进行检索
这里我们简单的写了一个界面,对数据进行查询
import sys
import MySQLdb
import wx
import datetime
start = datetime.datetime.now()
'''
处理数据库类
'''
class database:
def __init__(self):
self.con = MySQLdb.connect("127.0.0.1", "admin", "root", "zhwiki", charset='utf8mb4')
self.cursor = self.con.cursor()#数据库连接
def show(self,event):
table = Input.GetValue()
sql = "select * from review where Article_title ="+"'"+table+"'"#查询操作
print(table)
self.cursor.execute(sql)
result = self.cursor.fetchall()
contents.AppendText("That's all the data about: "+table+' \n')
for var in result:
for item in var:
contents.AppendText(str(item)+' , ')
contents.AppendText('\n')
end = datetime.datetime.now()#程序运行结束时间
print(end - start)
if __name__ == '__main__':
solve = database()
try:
#创建一个简单的查询窗口
app = wx.App()
win = wx.Frame(None,title='DadaBase',size=(410,335))#初始化窗口大小
bkg = wx.Panel(win)
showButton = wx.Button(bkg,label = 'Show')#设置查询按钮
showButton.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON,solve.show)
Input = wx.TextCtrl(bkg)
contents = wx.TextCtrl(bkg,style = wx.TE_MULTILINE | wx.HSCROLL)
hbox = wx.BoxSizer()
hbox.Add(Input, proportion=1,flag = wx.EXPAND)
hbox.Add(showButton, proportion=0, flag=wx.LEFT, border=5)
vbox=wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL)
vbox.Add(hbox, proportion=0, flag=wx.EXPAND | wx.ALL, border=5)
vbox.Add(contents, proportion=1, flag = wx.EXPAND | wx.LEFT | wx.BOTTOM | wx.RIGHT, border=5)
bkg.SetSizer(vbox)
win.Show()
app.MainLoop()
finally:
solve.cursor.close()
solve.con.close()
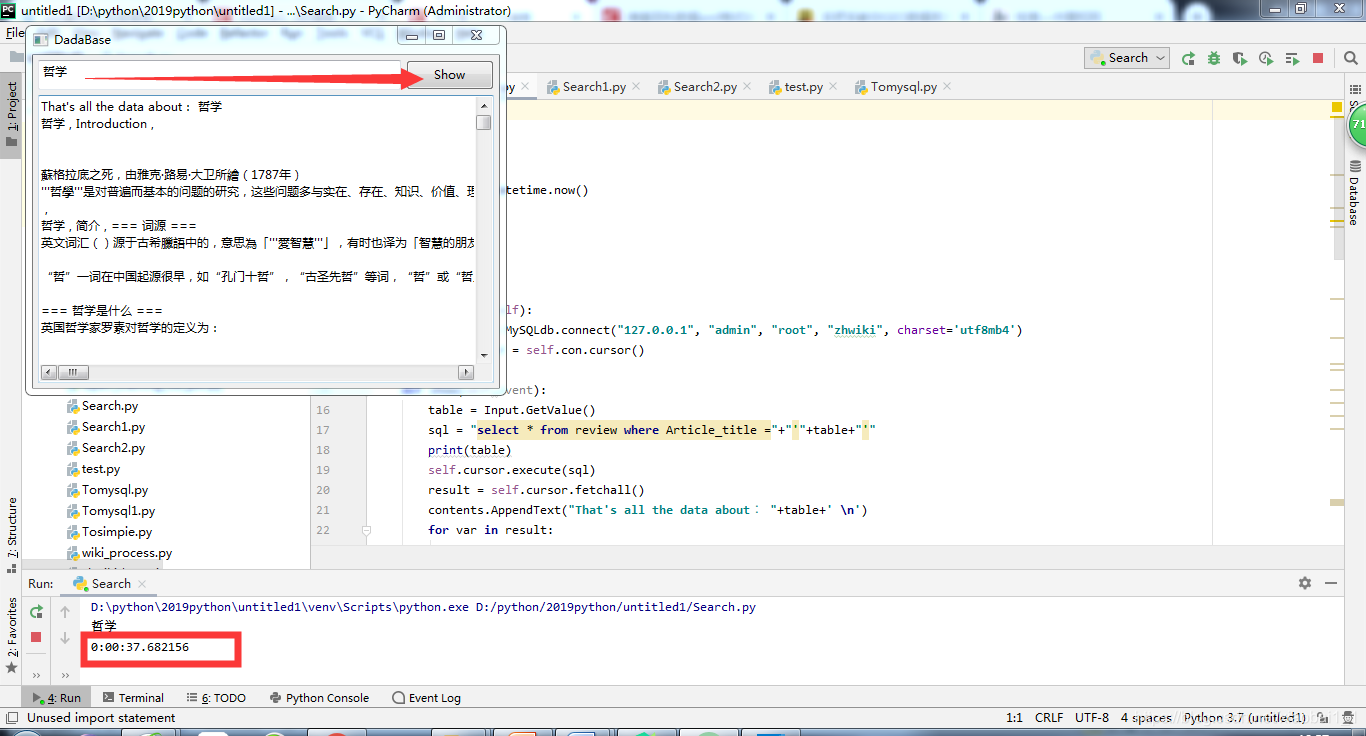
到这里我们就大功告成了,但是数据的查询时间还可以进一步优化
例如:
a.我们在创建表时应该建立索引
b.任何地方都不要使用 select * from table,用具体的字段列表代替 “ * ”,不要返回用不到的任何字段
c.应尽量避免在 where 子句中使用 != 或 <> 操作符,否则将引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描等等
d.应尽量避免在where子句中对字段进行函数操作
e…
注意:
前面程序里的import导入的MySQLdb、pymysql等如果你之前没有导过,那么你需要在运行程序前进行install
版权声明:本文为xiaobai1_1原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。