| 原文 | 翻译 |
| Yum is the Red Hat package manager that is able to query for information about available packages, fetch packages from repositories, install and uninstall them, and update an entire system to the latest available version. Yum performs automatic dependency resolution when updating, installing, or removing packages, and thus is able to automatically determine, fetch, and install all available dependent packages. | Yum是一个Red Hat包管理器,能够查询可用包的信息,从仓库获取包,安装和卸载他们,将这个系统升级到最新可用版本.yum在升级,安装和删除包时自动解决依赖问题,也就是能够自动决定,获取和安装所有依赖的包 |
| Yum can be configured with new, additional repositories, or package sources, and also provides many plug-ins which enhance and extend its capabilities. Yum is able to perform many of the same tasks that RPM can; additionally, many of the command-line options are similar. Yum enables easy and simple package management on a single machine or on groups of them. | Yum可以配置新的,额外的仓库或者包源,也提供很多插件来增强和扩展它的能力.Yum能够相同的执行很多RPM能够执行的任务并且很多命令行选项也类似.Yum让一台机器或一组机器的包管理变得简单. |
| The following sections assume your system was registered with Red Hat Subscription Management during installation as described in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Installation Guide. If your system is not subscribed, see Chapter 7, Registering the System and Managing Subscriptions. | 下面的章节假设你的系统已经像
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Installation Guide描述的那样已经在安装的时候在 RedHat订阅管理中注册了.如果你的系统没有订阅,参见. Chapter 7, Registering the System and Managing Subscriptions. |
|
Important Yum provides secure package management by enabling GPG (Gnu Privacy Guard; also known as GnuPG) signature verification on GPG-signed packages to be turned on for all package repositories (package sources), or for individual repositories. When signature verification is enabled, yum will refuse to install any packages not GPG-signed with the correct key for that repository. This means that you can trust that the RPM packages you download and install on your system are from a trusted source, such as Red Hat, and were not modified during transfer. See Section 9.5, “Configuring Yum and Yum Repositories” for details on enabling signature-checking with yum. |
重要信息: Yum通过GPG签名验证来提供包管理的安全性,它对所有打开验证的包源或独立的包源的包进行GPG签名验证.当签名验证启用时,yum会拒绝安装和源签名不一致的包.这意味着你可以相信你下载和撞到到你系统的RPM包来自一个可信任的源,例如Red Hat,并且传输中也没有被修改.参见配置Yum和Yum源来获取细节和启用yum签名检查 |
| Yum also enables you to easily set up your own repositories of RPM packages for download and installation on other machines. When possible, yum uses parallel download of multiple packages and metadata to speed up downloading. | Yum也让你轻松的设置你自己的RPM包源来下载和安装到其他机器.当可能的时候,yum使用多个包和元数据的并行下载来加速下载. |
| Learning yum is a worthwhile investment because it is often the fastest way to perform system administration tasks, and it provides capabilities beyond those provided by the PackageKit graphical package management tools. | 学习yum是一件值得的事情因为它经常是进行系统管理的最快方式并且它额外提供了图形化包管理器没有的能力 |
|
Note You must have superuser privileges in order to use yum to install, update or remove packages on your system. All examples in this chapter assume that you have already obtained superuser privileges by using either the |
注意 你需要有超级用户的特权来使用yum安装,升级或者卸载你系统的包.这章里面所有的例子假设你已经通过su或者sudo指令获得超级用户特权 |
9.1. Checking For and Updating Packages |
9.1. 检查和更新包 |
| Yum enables you to check if your system has any updates waiting to be applied. You can list packages that need to be updated and update them as a whole, or you can update a selected individual package. | yum让你能检查你的系统是否有等待采用的更新.你可以列出所有需要被更新的包并且一起更新掉,你也可以更新一个选中的单独的包 |
9.5. Configuring Yum and Yum Repositories |
9.5.配置Yum和Yum仓库 |
|
Note To expand your expertise, you might also be interested in the Red Hat System Administration III (RH254) and RHCSA Rapid Track (RH199) training courses. |
注意: 为了扩展你的经验,你也许对 红帽系统管理和红帽系统快速跟踪培训课程感兴趣. |
The configuration information for yum and related utilities is located at /etc/yum.conf. This file contains one mandatory [main] section, which enables you to set yum options that have global effect, and can also contain one or more [repository] sections, which allow you to set repository-specific options. However, it is recommended to define individual repositories in new or existing .repo files in the /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory. The values you define in individual [repository] sections of the /etc/yum.conf file override values set in the [main] section. |
yum配置信息和相关工具在/etc/yum.conf.这个文件包括一个必须的让你对yum选项有全局效果的main章节,也可能包括一个或多个针对特定仓库生效的repository章节.无论如何,建议在/etc/yum.repos.d/文件夹里新增或存在的.repo文件里定义各个仓库.你定义在/etc/yum.conf文件单独repository章节里值会覆盖main章节里的值 |
|
This section shows you how to:
|
这个章节向你展示:
|
9.5.1. Setting [main] Options |
9.5.1. 设置main参数 |
The /etc/yum.conf configuration file contains exactly one [main] section, and while some of the key-value pairs in this section affect how yum operates, others affect how yum treats repositories. |
/etc.yum.conf配置文件有且仅有一个main章节,这个章节里某些键值对影响你如何yum如何操作,其他的影响yum如何对待仓库 |
You can add many additional options under the [main] section heading in /etc/yum.conf. |
你可以在/etc/yum.conf的头部main章节下添加很多额外的配置 |
A sample /etc/yum.conf configuration file can look like this: |
一个/etc/yum.conf配置文件的例子如下: |
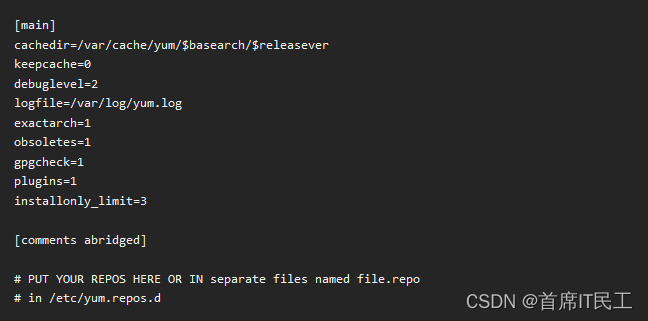 |
|
The following are the most commonly used options in the [main] section: |
下面是main章节里最常用配置项 |
|
The
|
assymeyes=值 assumeyes配置项决定了在关键操作的时候yum是否提出确认.使用下面的一个值替换 0(默认)–yum在执行关键操作时要求确认 1–如果设置assymeyes=1,在yum执行关键操作时不要求确认,yum的表象如同命令行参数-y和–assymeyes |
|
Use this option to set the directory where yum stores its cache and database files. Replace directory with an absolute path to the directory. By default, yum’s cache directory is See Section 9.5.3, “Using Yum Variables” for descriptions of the |
cachedir=文件夹 使用这个选项设置yun存储它的缓存和数据库文件的文件夹.用这个文件夹的决定路径替换文件夹.默认情况,yum的缓存文件夹是
|
|
This option specifies the detail of debugging output produced by yum. Here, value is an integer between |
这个选项指明了yum调试输出的细节.这里,值是一个在1到10的整数.设置一个高的 |
|
With this option, you can set yum to consider the exact architecture when updating already installed packages. Replace value with:
|
通过这个选项,你可以在升级已安装包时让yum考虑特定的架构,可以使用下列值: 0–在升级包时不要考虑对应架构 1(默认)–升级包时考虑对应架构.通过这个设定,yum不会在64位架构的系统上把一个已安装包升级为32位系统的包 |
|
The |
exclude=包名 更多包名 exclude选项让通过关键词在安装或者升级时排除包.通过应用一个空格分隔的包列表列出多个需要排除的包.允许使用shell的glob表达式(例如*和?) |
|
Use the
If this option is set in the |
gpgcheck=值 使用gpgcheck选项来具体说明yum应当对包进行GPG签名检查.可以使用以下值: 0–对所包,包括本地包安装禁用GPG签名检查 1(默认值)–对所有仓库,包括本地仓库安装包启用GPG签名检查.当gpgcheck启用时所有包的签名都被检查 如果这个选项设置在/etc/yum.conf文件的main章节,所有仓库都设置GPG检查规则.但是,你也可以对单独的仓库设置 |